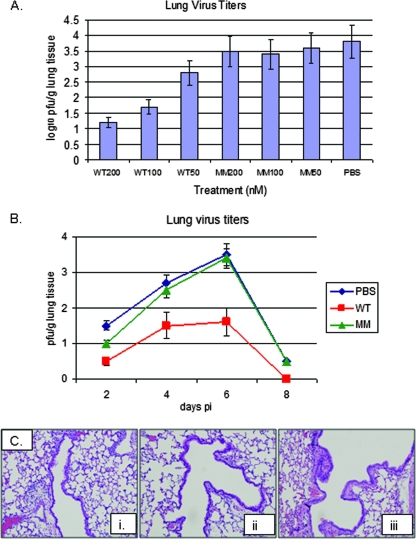
FIG. 1.
Prophylactic siRNA treatment reduces virus lung titers. (A) Mice were prophylactically treated i.n. with 4, 2, or 1 mg/kg of WT siRNA (WT200, WT100, or WT50, respectively) or MM siRNA (MM200, MM100, or MM50, respectively) or with PBS for 12 h prior to RSV/A2 infection (106 PFU). Lungs were harvested at day 4 p.i., and virus titers were determined by immunostaining plaque assay with anti-F protein monoclonal antibody (clone 131-2A) as previously described (64). The data are presented as the mean log10 PFU/g titer ± the standard error (SE; n = five mice/treatment/time point) in three separate experiments. The limit of virus detection is between 5 and 10 PFU/g of lung tissue. (B) To evaluate the kinetics of siRNA efficacy, mice were i.n. treated with 2 mg of WT or MM siRNA/kg or PBS vehicle and at 12 h posttreatment i.n. infected with 106 PFU of RSV/A2. Lungs were collected at day 2, 4, 6, or 8 p.i. and assayed by immunostaining plaque assay using Vero cells as previously described (64). (C) Lung histological pathogenesis was evaluated in WT siRNA-treated (i), PBS-treated (ii), and MM siRNA-treated (iii) mice at day 6 p.i. as previously described (26). Asterisks indicate a significant (P < 0.01) difference from the control.