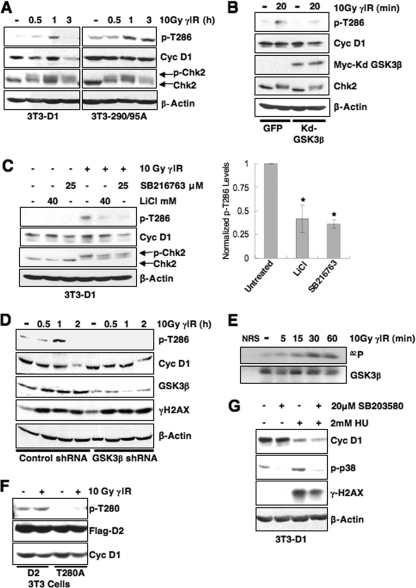
FIG. 4.
GSK3β catalyzes rapid cyclin D1 T286 phosphorylation following DNA damage. (A) Cyclin D1 phosphorylation is induced by DNA damage. Asynchronous 3T3-D1, 3T3-D1-290/95A, or 3T3-D1T286A were subjected to γIR, and immunoblots were performed with antibodies specific to p-T286, cyclin D1, and γH2AX. (B) Expression of kdGSK3β abrogates cyclin D1 phosphorylation following γIR. Lysates NIH 3T3 cells transiently expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) or kdGSK3β plus GFP and γ-irradiated were blotted for p-T286, cyclin D1, and myc to detect myc-tagged kdGSK3β. (C) Inhibition of GSK3β attenuates cyclin D1 phosphorylation following DNA damage. 3T3-D1 cells were pretreated with the GSK3β inhibitor LiCl or SB216763, followed by γIR and recovery for 30 min. Cyclin D1 phosphorylation was assessed by immunoblot for p-T286 and total cyclin D1. Chk2 mobility shift and γH2AX indicate DSB induction. (D) shRNA-mediated knockdown of GSK3β attenuates cyclin D1 phosphorylation. 293T cells were transfected with control or GSK3β-specific shRNA, cyclin D1, and CDK4 constructs. Cells were subjected to γIR and recovery for the times indicated, and cyclin D1 phosphorylation, efficiency of GSK3β knockdown, and checkpoint activation were assessed by immunoblotting. (E) GSK3β is activated following DNA damage. Endogenous GSK3β precipitated from cells following γIR was utilized as a kinase for in vitro reactions with recombinant myelin basic protein substrate. (F) Cyclin D2 Thr-280 phosphorylation is not induced following DNA damage. NIH 3T3 cells were transiently transfected with wild-type or D2T280A. Cells were irradiated 48 h posttransfection; cyclin D2 phosphorylation was assessed by Western blotting, and probing for total flag-tagged cyclin D2 served as a loading and transfection control. (G) Cyclin D1 is rapidly degraded following DNA damage in the presence of p38 inhibitor. Synchronous NIH 3T3 cells were pretreated with 20 μM SB203580 or DMSO for 30 min, followed by HU treatment for 2.5 h. Cell lysates were prepared and probed for p-p38 and cyclin D1.