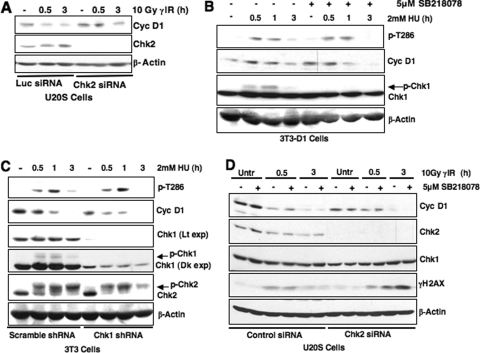
FIG. 7.
Examining the role of Chk1 and Chk2 kinases in cyclin D1 regulation. (A) Chk2 knockdown modestly attenuates DNA damage-induced cyclin D1 degradation. U20S cells were transiently transfected with Chk2-specific or luciferase control siRNAs. At 60 h posttransfection, the cells were gamma-irradiated, and cyclin D1 levels were assessed. (B and C) Chk1 activation is not required for cyclin D1 phosphorylation. Synchronous 3T3-D1 cells were pretreated with the Chk1 inhibitor SB218078 for 30 min (B), or NIH 3T3 cells were transduced with Chk1 shRNA lentivirus (C). Cells were treated with HU, and cyclin D1 phosphorylation or total protein levels were assessed by immunoblotting. (D) Chk1 and Chk2 activity is not synergistic in regulating cyclin D1. U20S cells expressing Chk2-specific siRNA were treated with the Chk1 inhibitor SB218078. Cyclin D1 levels were assessed by immunoblotting following DNA damage.