Fig. 1.
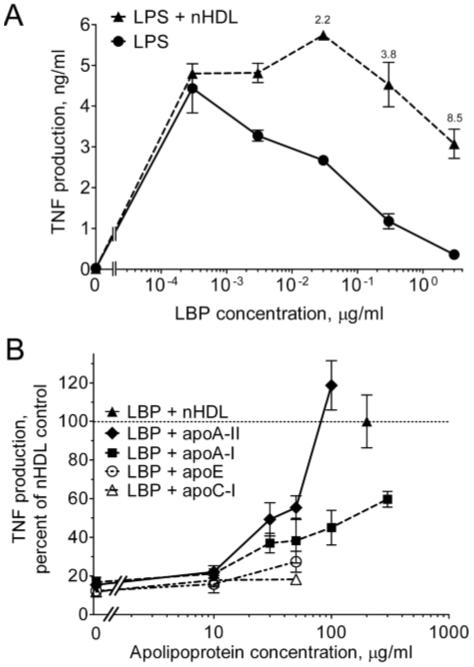
The apoA-II component of nHDL prevents the inhibition of LPS bioactivity by LBP. (A) THP-1 cells were incubated for 4 h at 37°C in the presence or absence of nHDL (200 μg protein/ml) and the indicated concentrations of LBP in SFM containing 20 pg/ml of LPS. TNF was measured in the culture supernatants by ELISA. Error bars denote mean ± range of duplicate determinations in a single experiment. TNF was undetectable in the absence of LPS and in the presence of nHDL alone (not shown). Annotations above the symbols denote the fold increase induced by nHDL. The experiment was repeated with similar results. (B) THP-1 cells were incubated with LPS in the presence of increasing concentrations of the indicated apolipoproteins or nHDL (200 μg/ml) in SFM containing an inhibitory concentration of LBP (1 μg/ml). The data are expressed as the percentage of the fold augmentation of TNF obtained with nHDL. Error bars are mean ± SEM of 3-5 experiments performed in duplicate. The dashed line (denoting 100%) indicates the activity of nHDL.
