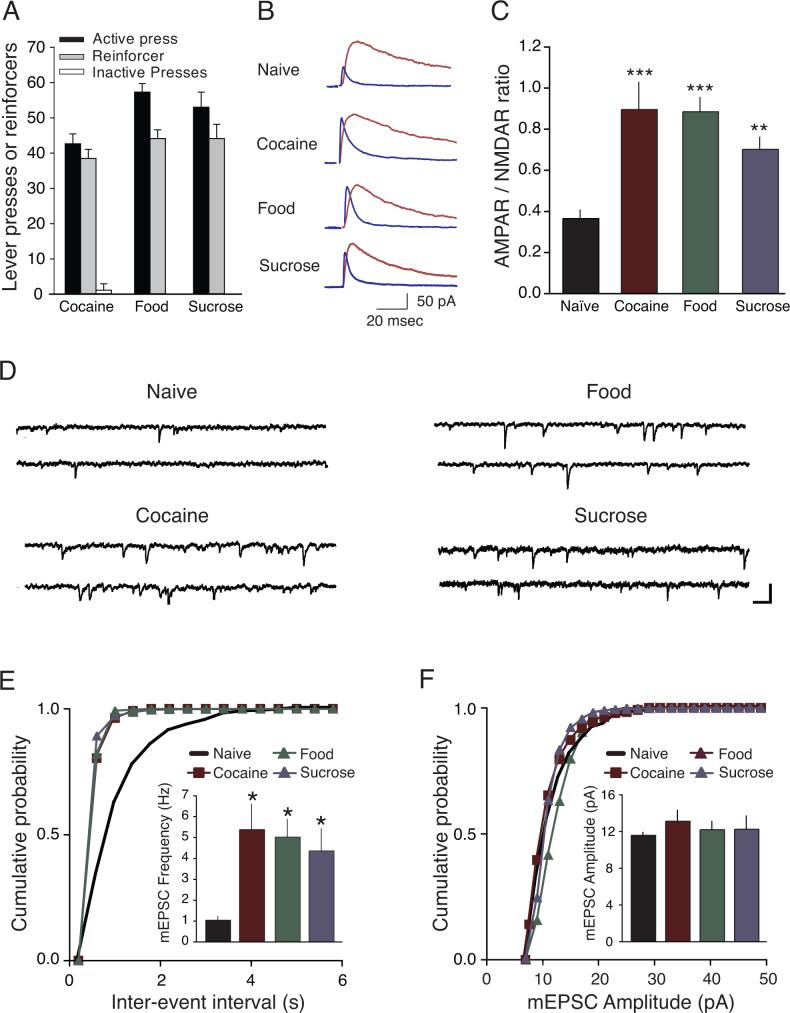
Figure 1.
Glutamatergic strength onto VTA DA neurons was enhanced one day after completion of cocaine, food, or sucrose self-administration. (A) Behavioral responses on the last day of training session in Cocaine, Food, and Sucrose groups. Active lever presses were 43 ± 3 presses for cocaine (n = 8 rats) 57 ± 2 presses for Food (n=11), and 53 ± 4 presses for Sucrose (n = 8). Cocaine rats earned 38 ± 3 infusions of cocaine (0.25 mg/kg/infusion), Food rats earned 44 ± 2 pellets of food, and Sucrose rats earned 44 ± 4 pellets of sucrose. Inactive lever responses averaged less than 3 presses for all groups. (B) Sample traces showing AMPAR- and NMDAR-mediated currents from Naïve rats and each of the self-administering groups. (C) Averaged AMPAR/NMDAR ratio from Naïve, Cocaine, Food, or Sucrose self-administrating rats. (D) Example traces of mEPSCs from Naïve, Cocaine, Food, and Sucrose groups. Scale bars, 20pA, 100 msec. Cumulative probability of frequency (E) and amplitude (F) of example cells from each of the four groups. Inset: averaged mEPSC frequencies were significantly increased in Cocaine, Food, and Sucrose rats compared with Naive rats, mEPSC amplitudes were not significantly different between the groups. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus Naive.