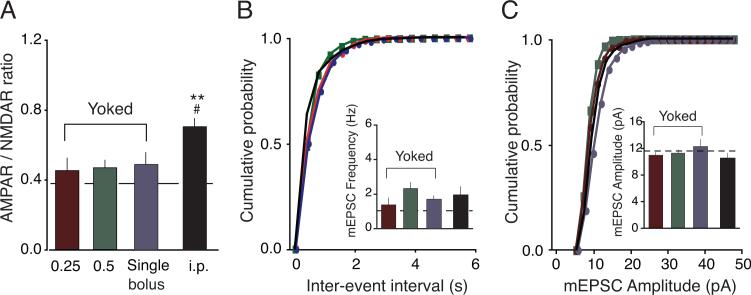
Figure 2.
Non-contingent cocaine delivery induced differential changes in glutamate function relative to voluntary cocaine self-administration. (A) Averaged AMPAR/NMDAR ratios from rats that received yoked cocaine (0.25 or 0.5 mg/kg/infusion, or a single i.v. bolus) were not significantly increased compared to Naïve rats. However, rats that received cocaine i.p. injections exhibited increased AMPAR/NMDAR ratios (B) Cumulative probability of frequency and amplitude (C) of example cells from each of the four groups. (Inset) Averaged mEPSC frequencies (B) and amplitudes (C) were not significantly different in rats that received cocaine noncontingently. Dotted lines represent averaged value from Naïve rats. **p < 0.01 versus Naïve, #p < 0.05 versus yoked groups.