Fig. 1.
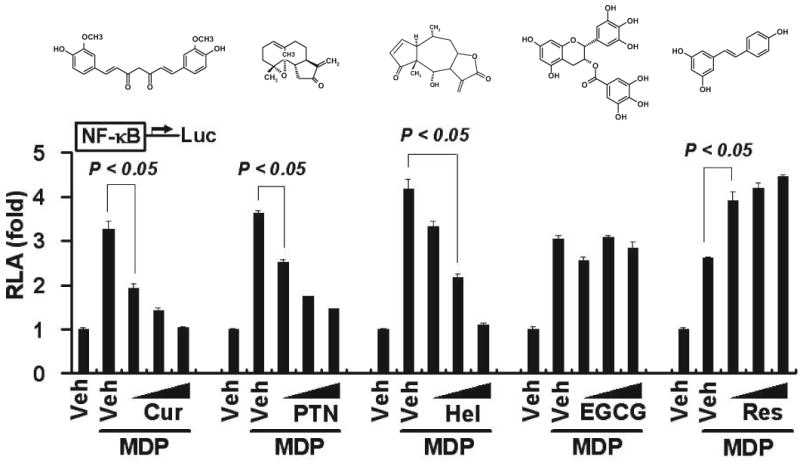
Curcumin inhibits MDP-induced NF-κB activation. HCT116 cells were transfected with NF-κB-luciferase and β-galactosidase reporters. After 24 h, the cells were pretreated with curcumin (10, 20, and 30 μM), parthenolide (5, 10, and 15 μM), helenalin (1, 3, and 5 μM), EGCG (10, 30, and 50 μM), or resveratrol (10, 30, and 50 μM) for 1 h and then coincubated with 50 μM MDP for additional 6 h. Cell lysates were prepared and luciferase and β-galactosidase enzyme activities measured as described under Materials and Methods. Relative luciferase activity (RLA) was normalized with β-galactosidase activity. Values are mean ± S.E.M (n = 3). Statistical significant difference (p < 0.05) is indicated between cells treated with MDP alone and cells treated with MDP plus the indicated phytochemicals. Cur, curcumin; PTN, parthenolide; Hel, helenalin; and Res, resveratrol. The molecular structure is shown above the reporter assay data for each of the phytochemicals.
