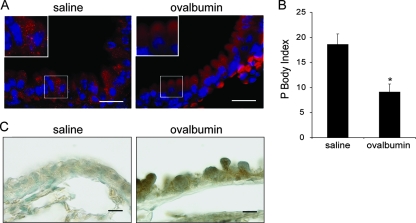
FIG. 7.
Change in P-body number in mouse activated bronchial airway epithelium. BALB/c mice were sensitized with ovalbumin, and then the airways were challenged with either saline or ovalbumin. (A) High magnification of bronchial airways from mice challenged with saline or ovalbumin and then subjected to immunofluorescence using rabbit anti-Dcp1a antibody to detect P bodies (red signal). Blue signal, DAPI-stained nuclei. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Quantification of P bodies in bronchial epithelial cells was determined by counting the number of bronchial epithelial cells per millimeter of airway basement membrane that contained 20 or more P bodies (P-body index) using ImagePro Plus software (Media Cybernetics). Data are presented as the mean P-body index ± standard error of the mean (n = 4 mice per group). The asterisk denotes a significant difference. (C) Sections from the same mice described in panel A were stained with an antibody against MCP-1 followed by immunoperoxidase detection (shown in brown). Scale bar, 100 μm.