Abstract
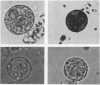
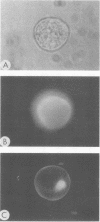
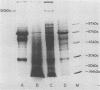
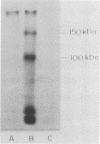
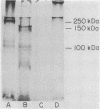
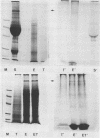
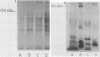
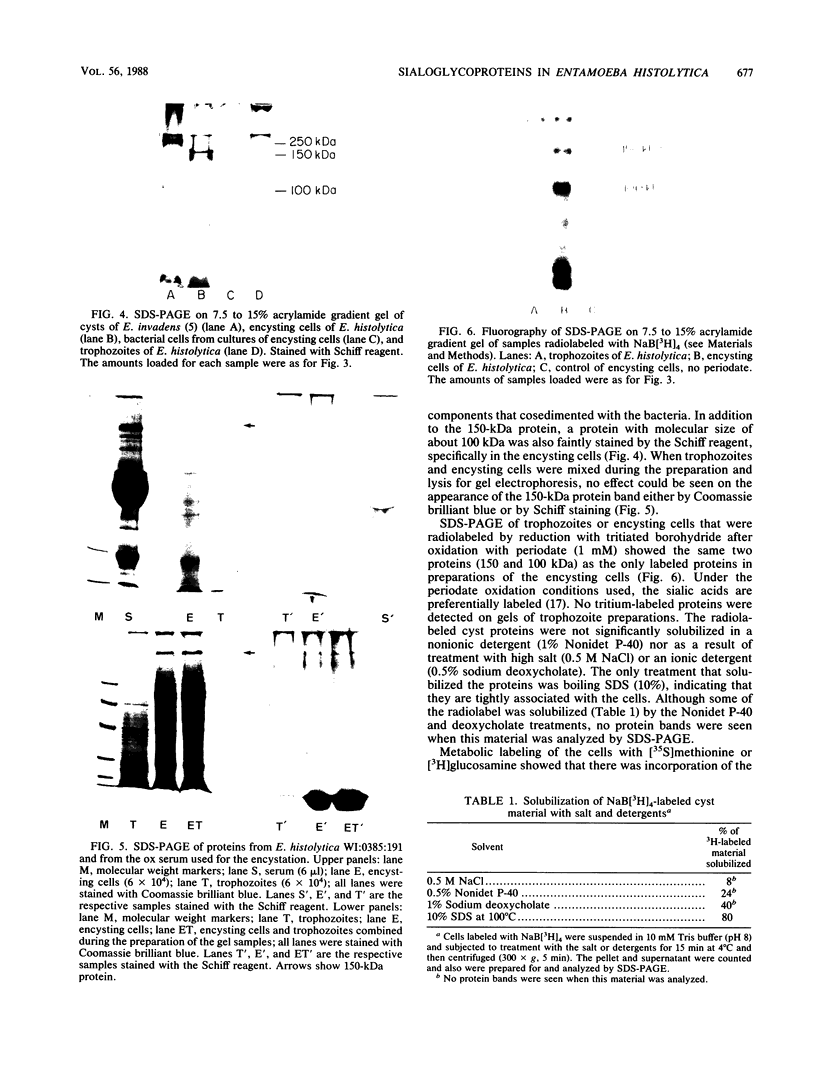
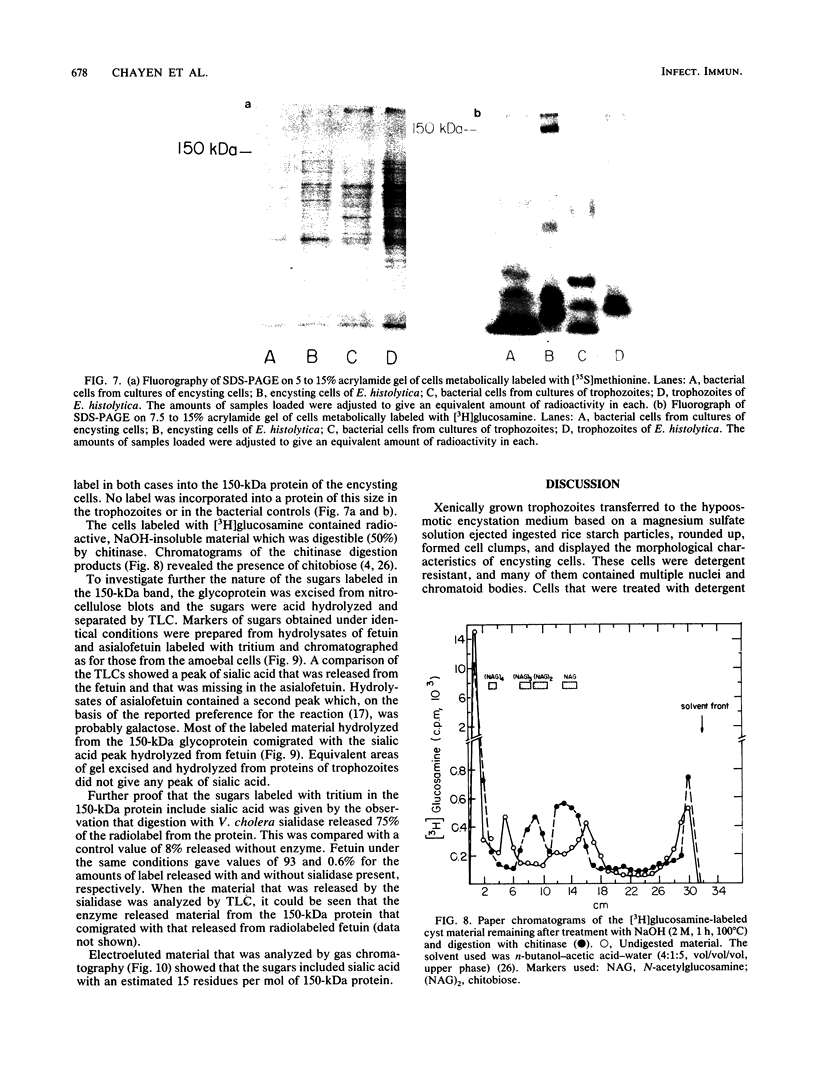
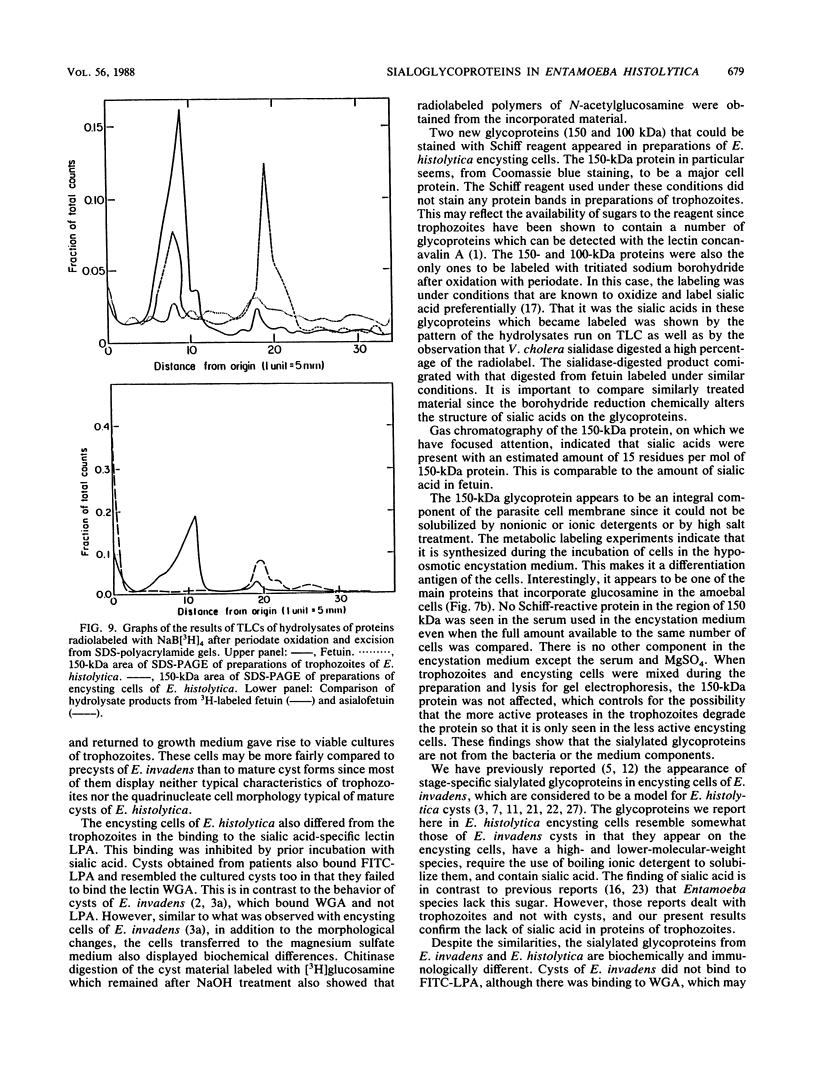
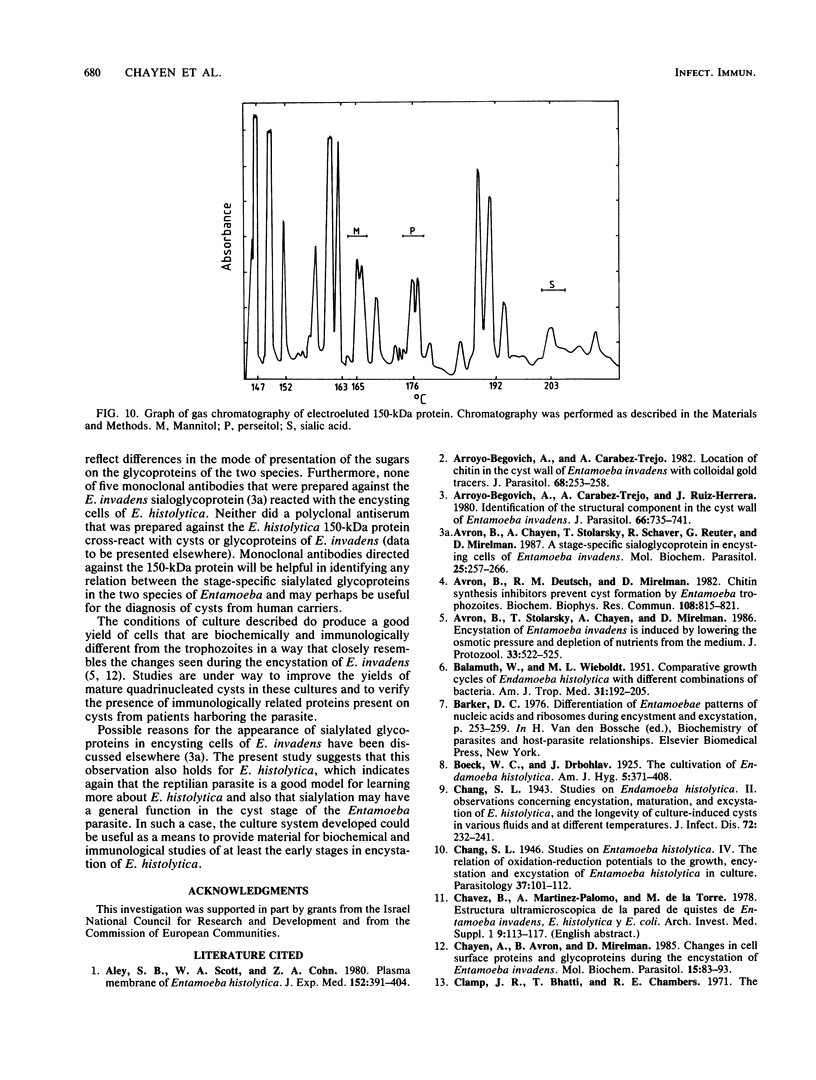
Amoeba-bacterium cultures of Entamoeba histolytica transferred to a hypoosmotic medium depleted of nutrients changed morphologically and biochemically. The cells ejected grains of rice starch, rounded up, and formed a distinct cell wall that was resistant to detergent, bound the sialic acid-specific lectin from Limulus polyphemus, and became fluorescent with Calcofluor M2R. A subpopulation of these cells displayed more than one nucleus. All these signs are characteristic of encysting cells and were also observed in cysts obtained from a human patient. The morphological changes were accompanied by the appearance of two new glycoproteins with apparent molecular sizes of 100 and 150 kilodaltons which contained sialic acid. Sialic acid has been reported to be absent from trophozoites of Entamoeba species. The presence of this sugar residue on cyst-specific proteins parallels recently reported findings during the encystation of the related reptilian parasite Entamoeba invadens. This may indicate a basic role for sialic acid in the encystation of Entamoeba parasites.
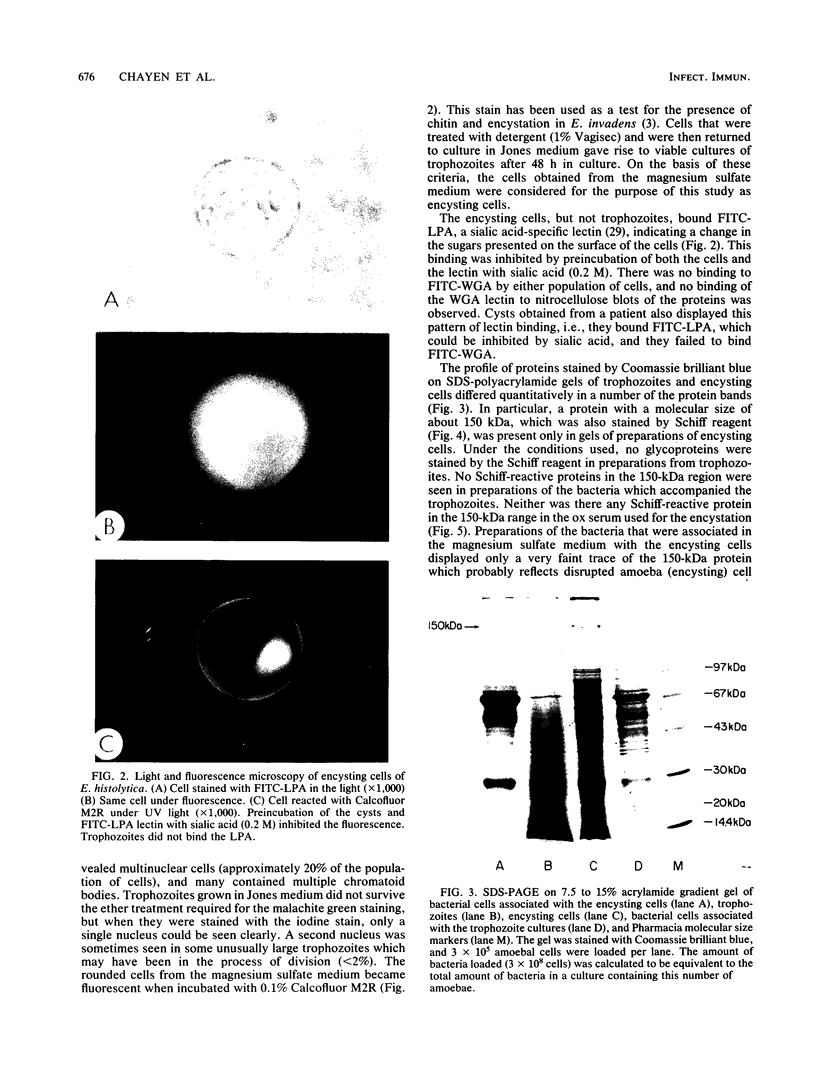
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aley S. B., Scott W. A., Cohn Z. A. Plasma membrane of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):391–404. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo-Begovich A., Cárabez-Trejo A. Location on chitin in the cyst wall of Entamoeba invadens with colloidal gold tracers. J Parasitol. 1982 Apr;68(2):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo-Begovich A., Cárabez-Trejo A., Ruíz-Herrera J. Identification of the structural component in the cyst wall of Entamoeba invadens. J Parasitol. 1980 Oct;66(5):735–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avron B., Chayen A., Stolarsky T., Schauer R., Reuter G., Mirelman D. A stage-specific sialoglycoprotein in encysting cells of Entamoeba invadens. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Oct;25(3):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avron B., Deutsch R. M., Mirelman D. Chitin synthesis inhibitors prevent cyst formation by Entamoeba trophozoites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 30;108(2):815–821. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90902-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avron B., Stolarsky T., Chayen A., Mirelman D. Encystation of Entamoeba invadens IP-1 is induced by lowering the osmotic pressure and depletion of nutrients from the medium. J Protozool. 1986 Nov;33(4):522–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALAMUTH W., WIEBOLDT M. L. Comparative growth cycles of Endamoeba histolytica with different combinations of bacteria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1951 Mar;31(2):192–205. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1951.s1-31.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chayen A., Avron B., Mirelman D. Changes in cell surface proteins and glycoproteins during the encystation of Entamoeba invadens. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Apr;15(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chávez B., Martínez-Palomo A., De La Torre M. Estructura ultramicroscópica de la pared de quistes de Entamoeba invadens, E. histolytica y E. coli. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1978;9 (Suppl 1):113–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamp J. R., Bhatti T., Chambers R. E. The determination of carbohydrate in biological materials by gas-liquid chromatography. Methods Biochem Anal. 1971;19:229–344. doi: 10.1002/9780470110386.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. A new liquid medium for xenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other lumen-dwelling protozoa. J Parasitol. 1982 Oct;68(5):958–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feria-Velasco A., Martínez-Zedillo G., Treviño-García Manzo, Gutiérrez-Pastrana M. D. Investigación de ácido siálico en la cubierta exterior de trofozoítos de E. histolytica. Estudio bioquimico y citoquímico de alta resolución. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1973;(Suppl):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Andersson L. C. Selective radioactive labeling of cell surface sialoglycoproteins by periodate-tritiated borohydride. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5888–5894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Spencer H. C., Jr, Healy G. R., Gleason N. N., Sexton D. J., Herron C. A. Amebiasis: epidemiologic studies in the United States, 1971-1974. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jan;88(1):89–97. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCONNACHIE E. W. Studies on Entamoeba invadens Rodhain, 1934, in vitro, and its relationship to some other species of Entamoeba. Parasitology. 1955 Nov;45(3-4):452–481. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000027803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnachie E. W. The morphology, formation and development of cysts of Entamoeba. Parasitology. 1969 Feb;59(1):41–53. doi: 10.1017/s003118200006981x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J., Meerovitch E. The surface membrane and cytoplasmic membranes of Entamoeba invadens (Rodhain 1934)-I. Gross chemical and enzymatic properties. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1975 Dec 15;52(4):477–486. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(75)90222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Wexler A., Chayen A. Changes in isoenzyme patterns of a cloned culture of nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica during axenization. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):827–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.827-832.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal R. A. Survival of Entamoeba and related Amoebae at low temperature. I. Viability of Entamoeba cysts at 4 degrees C. Int J Parasitol. 1974 Jun;4(3):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(74)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rengpien S., Bailey G. B. Differentiation of Entamoeba: a new medium and optimal conditions for axenic encystation of E. invadens. J Parasitol. 1975 Feb;61(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche A. C., Schauer R., Monsigny M. Protein-sugar interactions. Purification by affinity chromatography of limulin, an N-acyl-neuraminidyl-binding protein. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 1;57(3):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer R. Analysis of sialic acids. Methods Enzymol. 1987;138:132–161. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)38012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer R. Chemistry, metabolism, and biological functions of sialic acids. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1982;40:131–234. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer R., Reuter G., Mühlpfordt H., Andrade A. F., Pereira M. E. The occurrence of N-acetyl- and N-glycoloylneuraminic acid in Trypanosoma cruzi. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Aug;364(8):1053–1057. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.2.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G., Bhoyroo V. D. Structure of the O-glycosidically linked carbohydrate units of fetuin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5704–5717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Studies on fetuin, a glycoprotein of fetal serum. I. Isolation, chemical composition, and physiochemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1960 Oct;235(10):2860–2869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]