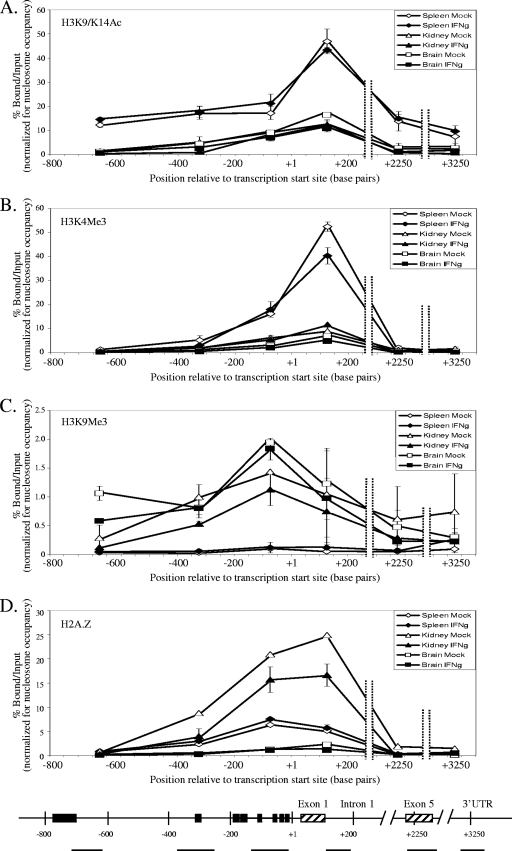
FIG. 6.
Histone modifications positively associated with transcription (H3K9/K14 acetylation [A] and H3K4 trimethylation [B]) are higher at the PD1 gene in highly expressing spleen cells than in lower expressing kidney or brain cells. On the other hand, kidney and brain have higher levels of a histone modification negatively associated with transcription (H3K9 trimethylation [C]). In contrast, H2A.Z occupancy (D) showed a unique tissue-specific pattern, where the kidney had the highest levels of H2A.Z, followed by the spleen, whereas the brain had very low levels of H2A.Z. Panels A to D show the percentage of bound versus input in mock-treated spleen (⋄), IFN-γ-treated spleen (⧫), mock-treated kidney (▵), IFN-γ-treated kidney (▴), mock-treated brain (□), and IFN-γ-treated brain (▪). The bottom panel shows the MHC class I gene with amplified regions (horizontal lines), important regulatory elements (▪), and exons (▒). The results are an average of two independent experiments. Error bars represent the standard errors of mean. Input is the entire mononucleosomal fraction before immunoprecipitation, and hence the results obtained are normalized to nucleosome occupancy. The lines drawn connecting data points do not necessarily imply levels between points.