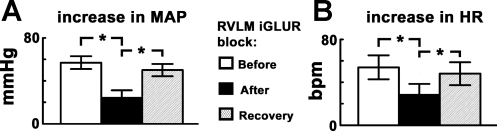
Fig. 1.
Cold pressor test (CPT) responses: effect of blockade of ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGLURs) in the rostral ventrolateral medullary (RVLM) pressor area. A and B: increases in mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) in response to initial CPT were 57.0 ± 6.0 mmHg and 54.0 ± 11.2 beats/min, respectively (n = 5). After the blockade of iGLURs in the RVLM, by microinjections of 2,3-dioxo-6-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo-[f]quinoxaline-7-sulfonamide disodium (NBQX; 2 mM, 50 nl) and d-(−)-2-amino-7-phosphono-heptanoic acid (d-AP7; 5 mM, 50 nl), the increases in MAP and HR in response to CPT were 25.0 ± 6.3 mmHg and 29.0 ± 9.5 beats/min, respectively; both MAP and HR responses to CPT after the blockade of iGLURs in the RVLM were significantly (*P < 0.05) smaller compared with the responses before the blockade. After ∼60 min, increases in MAP and HR in response to CPT were 50.0 ± 5.7 mmHg and 48.0 ± 10.6 beats/min, respectively, indicating recovery of responses.