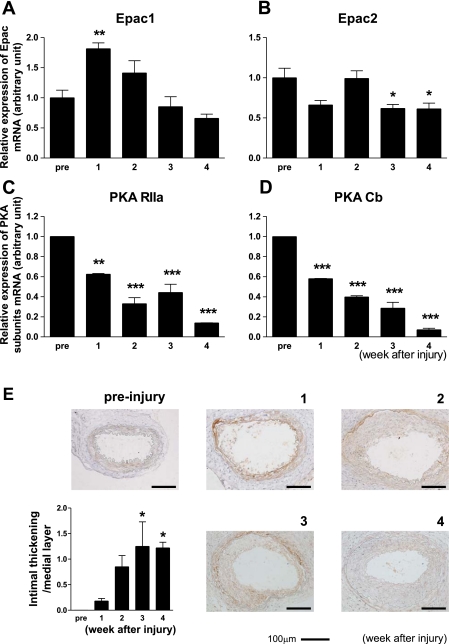
Fig. 1.
Changes in exchange protein activated by cAMP (Epac) and PKA expression upon vascular injury. A and B: Epac1 (A), but not Epac2 (B), mRNA increased after vascular injury. Transluminal mechanical injury of the femoral artery was induced by insertion of a large wire. mRNA expression of Epac1 was determined at 0 (pre), 1, 2, 3, and 4 wk by quantitative RT-PCR. The abundance of each mRNA was determined relative to GAPDH. Data are fold increases of control; n = 4. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. C and D: changes in PKA subunit mRNA expression after vascular injury. mRNA expression of α-regulatory (RIIa; C) and β-catalytic (Cb; D) subunits of PKA were determined in the same manner as that of Epac. Data are fold increases of control; n = 4. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. E: changes in Epac1 protein expression and intimal thickening after vascular injury. Immunohistochemistry with anti-Epac1 antibody was performed at 0 (pre), 1, 2, 3, and 4 wk after injury to the mouse femoral artery. Representative images are shown. The ratio of intimal thickening to the medial layer was increased in a tine-dependent manner. n = 7–9. *P < 0.05.