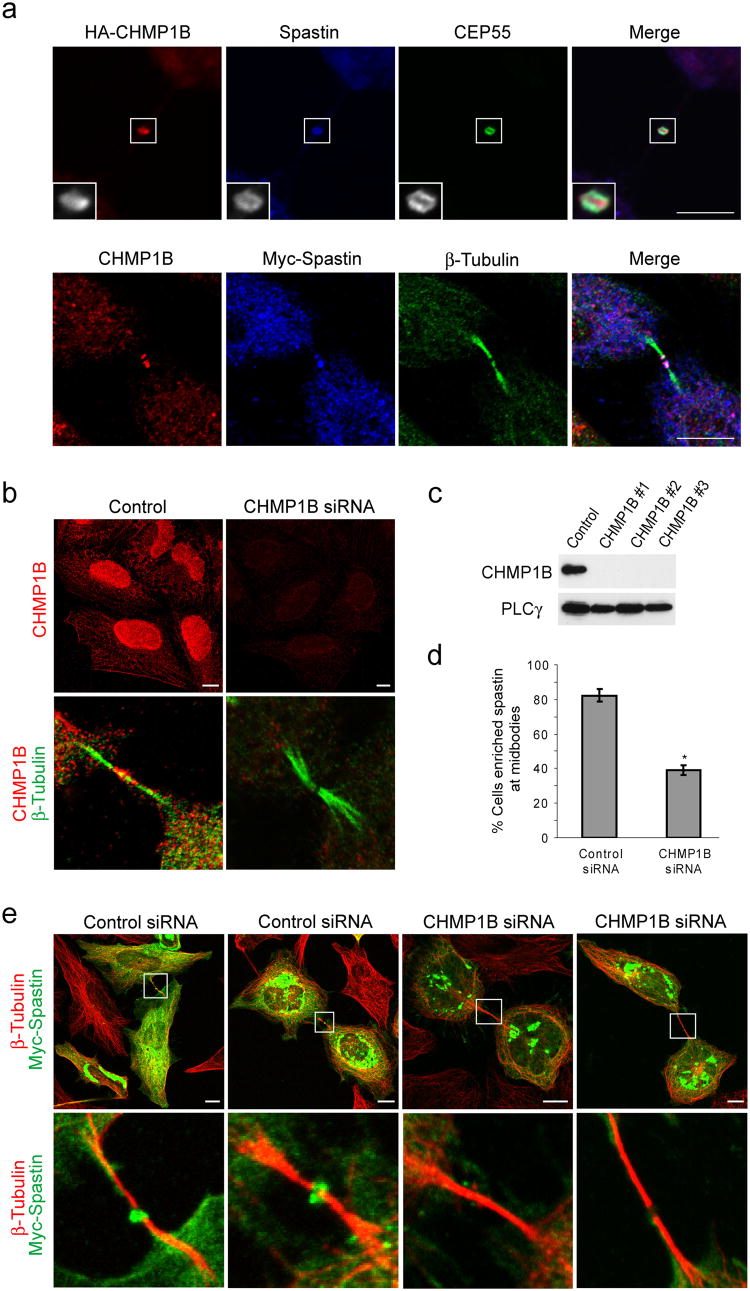
Figure 1. CHMP1B is present at midbodies and colocalizes with and recruits spastin.
(a) Top panels, HeLa cells expressing HA-CHMP1B were immunostained for HA-epitope (red) as well as endogenous spastin (blue) and CEP55 (green). Lower panels, Cells expressing Myc-Spastin were immunostained for endogenous CHMP1B (red), Myc-epitope (blue), and β-tubulin (green). Bar, 10 μm. (b) Lysates from HeLa cells transfected with either of three different siRNAs specific for CHMP1B or else control siRNA were immunoblotted for CHMP1B. Equal protein loading was monitored by immunoblotting for PLCγ. (c) HeLa cells transfected with control siRNA or CHMP1B siRNA #3 were immunostained with anti-CHMP1B antibodies (red; top panels). Enrichment of CHMP1B at midbodies, as revealed by β-tubulin co-staining (green; bottom panels), is substantially decreased in CHMP1B-depleted cells (red; bottom panels). Bar, 10 μm. (d and e) HeLa cells transfected with either control or CHMP1B siRNA were re-transfected with Myc-spastin. (d) Quantification of spastin enrichment at midbodies in CHMP1B or control siRNA treated cells (n=3; 100 cells per experiment; ±SD). *p<0.001. (e) Midbodies, as identified by β-tubulin staining (red), show a lack of spastin (green) enrichment in CHMP1B-depleted cells (right two panels) as compared with control cells (left two panels). The boxed area is enlarged in the lower panels. Bar, 10 μm.