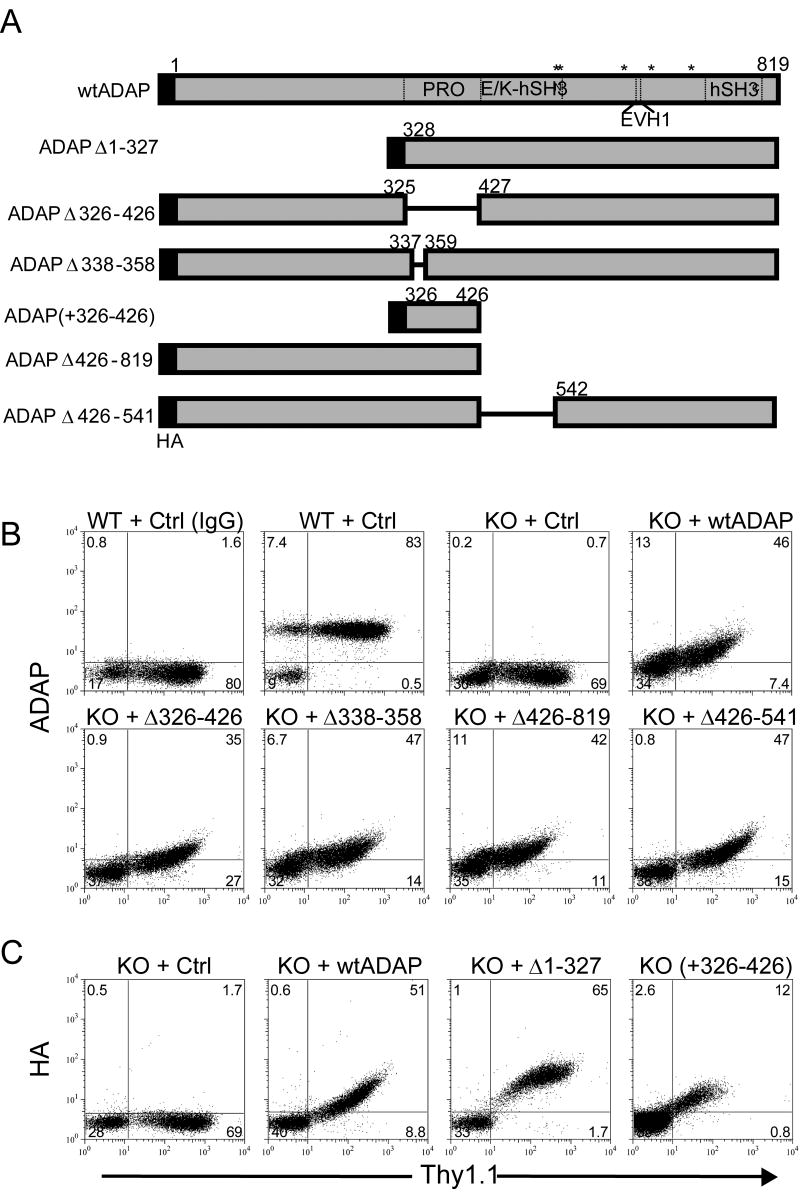
Figure 2. Schematic and expression of ADAP mutant constructs.
(A) Scale diagram of ADAP expression constructs used in this study. Amino acid numbering is given for the murine ADAP p130 isoform. Abbreviations: PRO, proline-rich domain; E/K, glutamic acid and lysine-rich domain; hSH3, N-terminal (N) or C-terminal (C) helical SH3 domain; EVH1, Ena/Vasp homology domain. Asterisks (*) are used to denote the position of tyrosines 547, 549, 584, 615, 687 found in phosphorylation consensus motifs. (B) Freshly harvested naïve DO11.10/hCAR/ADAP+/+ (WT) or ADAP-/- (KO) lymphocytes were transduced with adenoviruses encoding the indicated constructs or Thy1.1 control adenovirus (ctrl) and fixed and stained with an anti-Thy1.1 antibody and either anti-ADAP antibody or non-immune sheep serum (IgG) and analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Same as in (B) except the indicated constructs were stained with an anti-hemaglutinin (HA) antibody. Expression profiles are representative of at least three independent analyses performed for each construct shown.