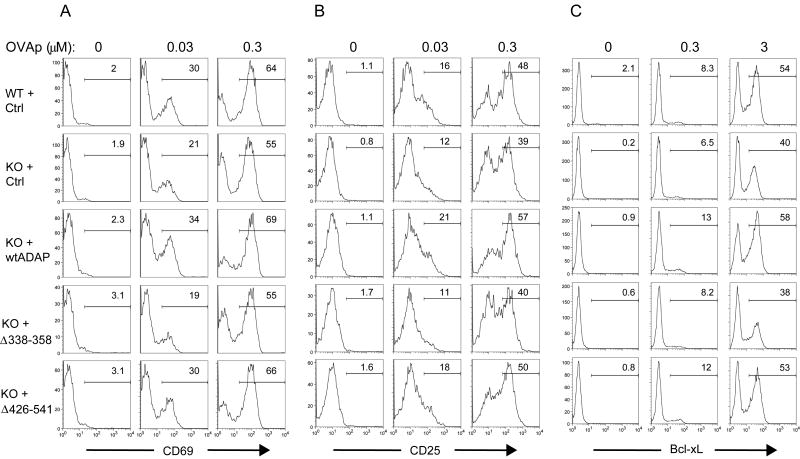
Figure 7. The ADAP proline rich domain is required for antigen-dependent T cell activation.
Naïve DO11.10/hCAR/ADAP+/+ (WT) or ADAP-/- (KO) lymphocytes expressing the indicated ADAP constructs were stimulated with fresh Balb/C splenocytes pulsed with the indicated doses of OVAp as described in Materials and Methods. (A-B) Cells were stimulated for 18h, stained for KJ-126, Thy1.1, CD69, and CD25 as indicated, fixed, and analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Cells were stimulated for 48h with OVAp, stained for KJ-126 and Thy1.1, fixed, permeablized with saponin, stained for anti-Bcl-xL, and analyzed by flow cytometry. (A-C) The percentage of CD69+, CD25+, or Bcl-xL+ cells within the KJ1-26+Thy1.1+ gate is shown on each histogram. Results are shown for a single representative experiment and are representative of at least four independent experiments performed for CD69 and CD25 and three experiments for Bcl-xL.