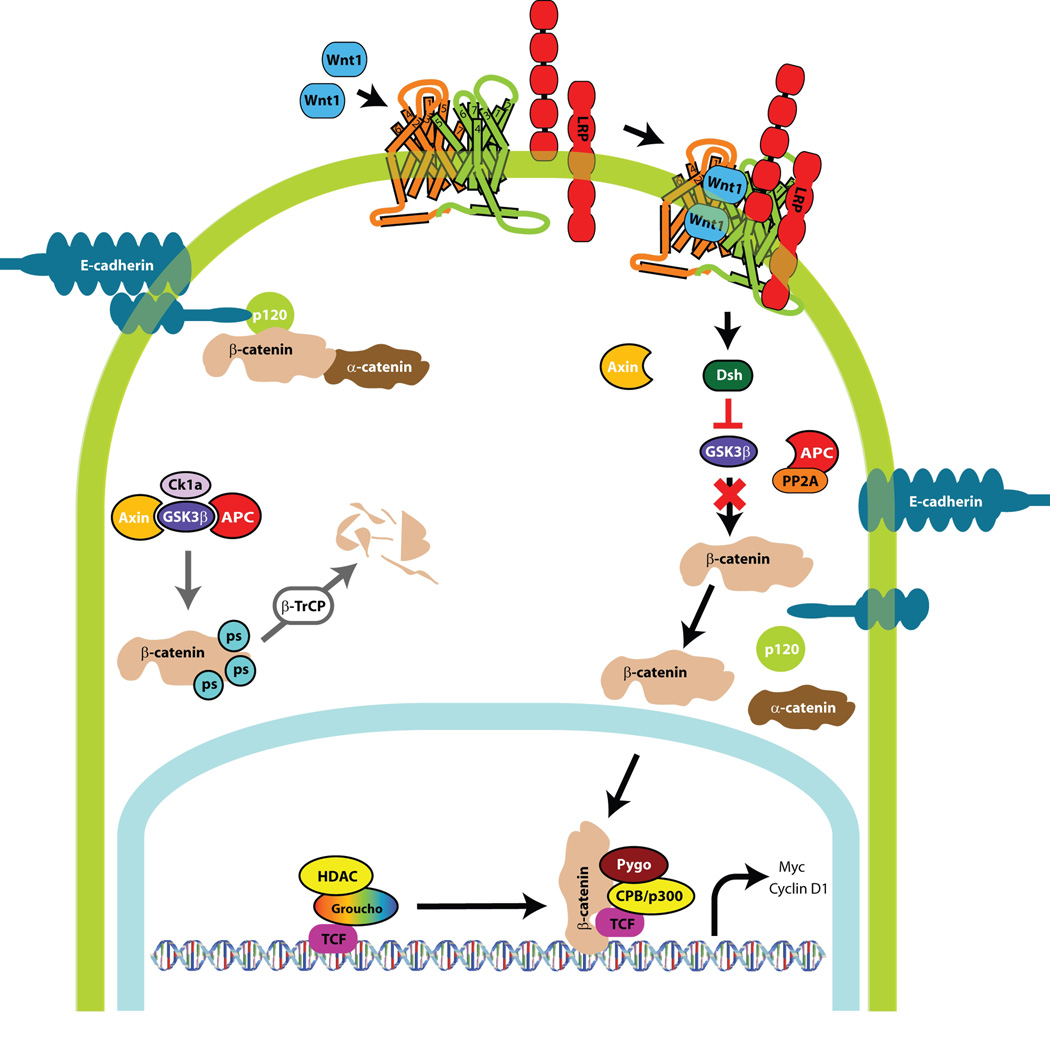
Figure 2. Wnt Signaling Pathway.
Wnt ligand interaction with the LRP receptor complex activates the pathway and β-catenin levels increase intracellularly. β-catenin translocates to the nucleus where it forms a transcriptional regulatory complex with TCF/LEF to activate transcription of cyclin D1, c-Myc and other downstream targets. E-cadherin negatively regulates Wnt signaling. E-cadherin binds and sequesters β-catenin to the plasma cell membrane at the adherens junctions, rendering it unavailable for transcriptional activity. Maintenance of low β-catenin levels by axin occur in the absence of Wnt ligand. Axin coordinates the β-catenin destruction complex (casein kinase 1a (Ck1a), glycogen synthase kinase 3β (Gsk3β), the tumor suppressor adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) and protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A)). Together, these components lead to the sequential phosphorylation of β-catenin and eventual proteasomal degradation.