Abstract
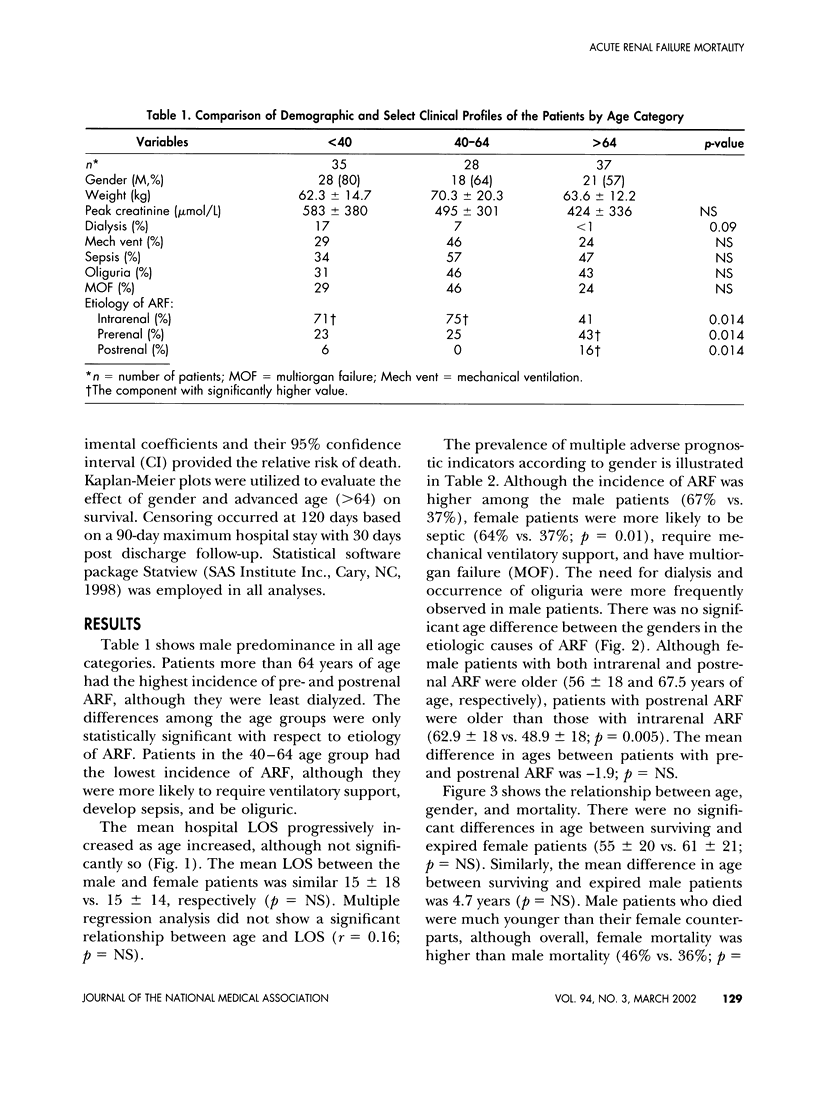
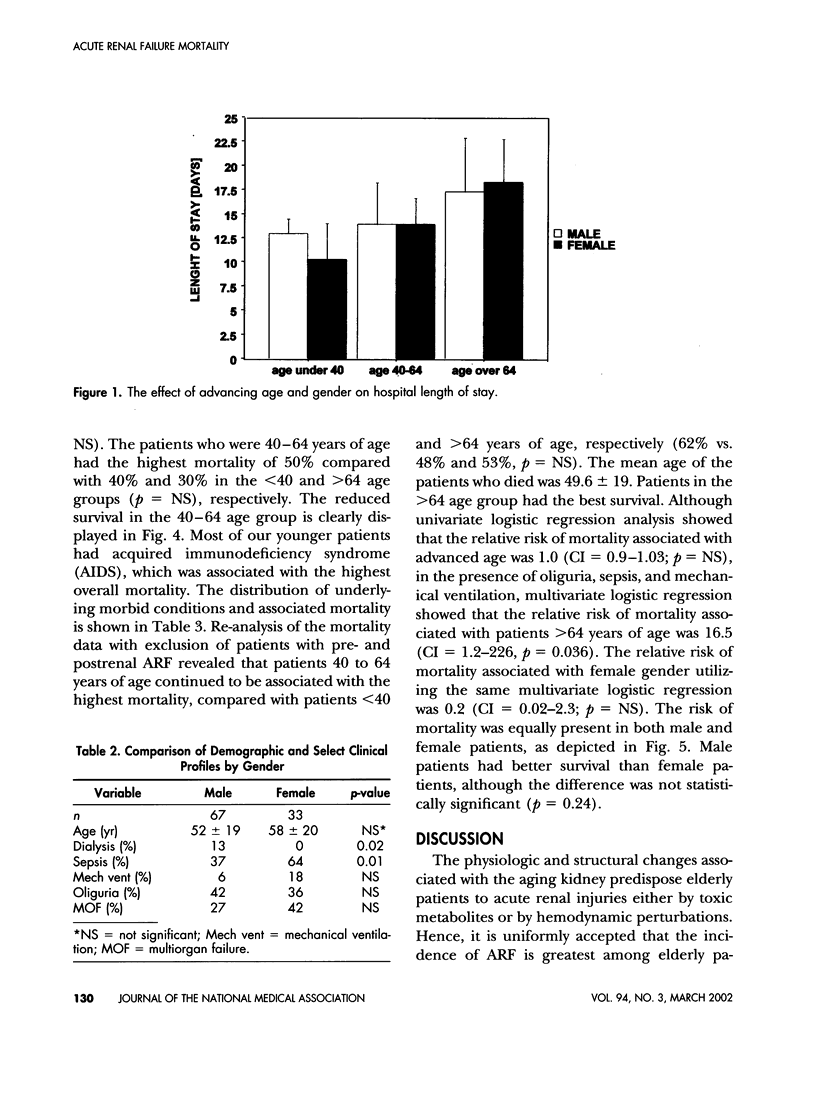
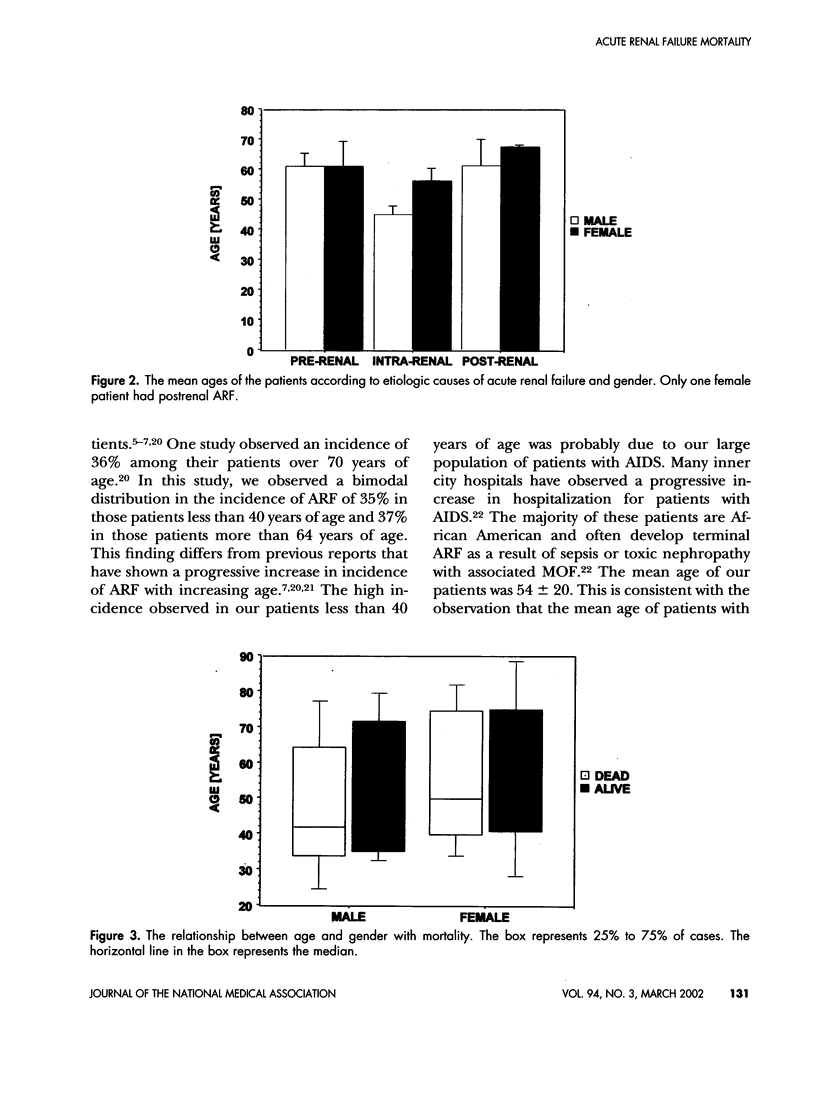
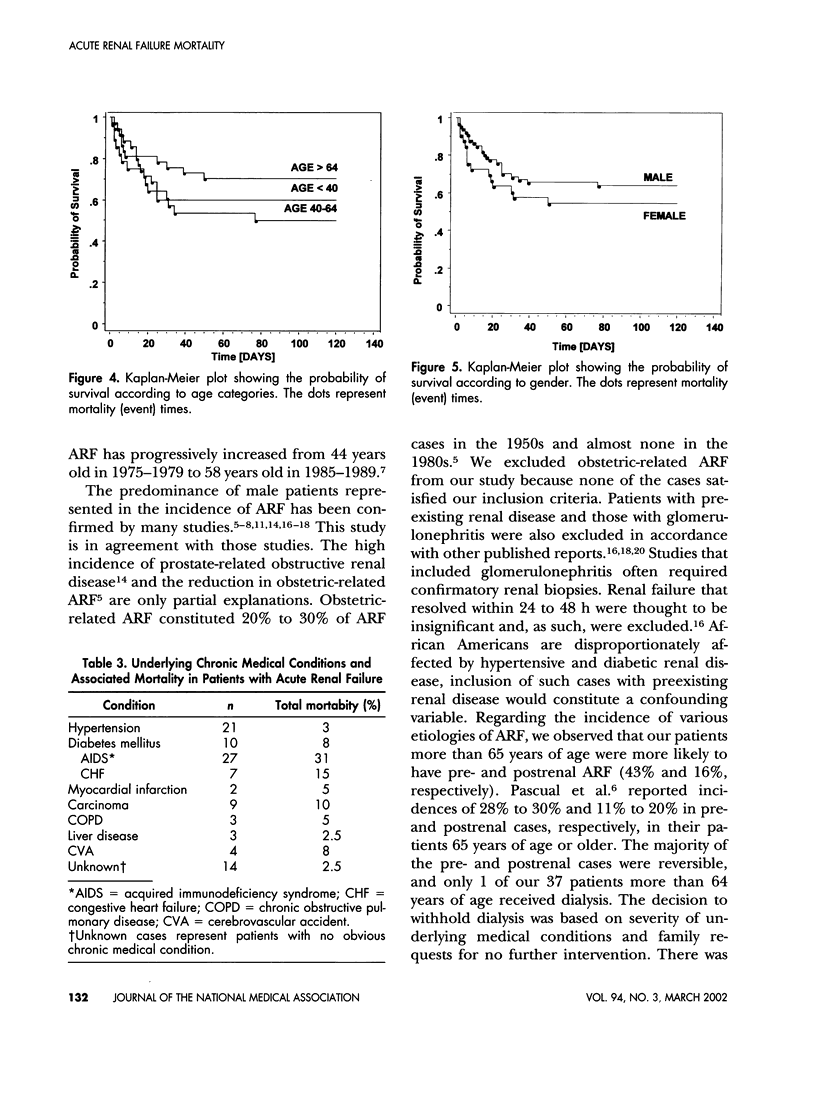
The aging kidney is at risk for both toxic and hemodynamic-induced acute damage, resulting in a high incidence of acute renal failure (ARF) in elderly patients. The effect of age and or gender in ARF mortality in African Americans (AA) was studied in a 3-year, computer assisted retrospective review. In an inner city medical center, 100 patients classified as ARF at discharge or expiration were included in the study. Patients were classified into 3 age categories: <40, 40-64, and >64 years. The incidence of ARF was 35%, 28% and 37%, respectively. Patients >64 years of age were less likely to be dialyzed. Both pre- and postrenal causes of ARF were more common in patients >64 years of age than in younger patients. Hospital length of stay increased progressively with age. Mortality was lower in patients >64 years of age than in younger patients. The incidence of ARF was higher in male than female patients and the incidence of sepsis was higher in female than male patients. Dialytic need was greater in male patients, but mortality was higher in female than male patients. Multivariate logistic regression showed that in the presence of sepsis, oliguria and mechanical ventilatory support, the relative risk of mortality associated with advanced age was 16.5, the relative risk of mortality associated with female gender was 0.2. In summary, hospitalized elderly African-American patients have a high incidence of ARF, and patients less than 40 years of age are equally at risk. Although mortality was higher in female patients, gender and advanced age did not independently contribute to high mortality. Neither age nor gender considerations should supplant sound clinical judgment in the management of and decision making in elderly African-American patients with ARF.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berisa F., Beaman M., Adu D., McGonigle R. J., Michael J., Downing R., Fielding J. W., Dunn J. Prognostic factors in acute renal failure following aortic aneurysm surgery. Q J Med. 1990 Jul;76(279):689–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesenbach G., Zazgornik J., Kaiser W., Grafinger P., Stuby U., Necek S. Improvement in prognosis of patients with acute renal failure over a period of 15 years: an analysis of 710 cases in a dialysis center. Am J Nephrol. 1992;12(5):319–325. doi: 10.1159/000168466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brivet F. G., Kleinknecht D. J., Loirat P., Landais P. J. Acute renal failure in intensive care units--causes, outcome, and prognostic factors of hospital mortality; a prospective, multicenter study. French Study Group on Acute Renal Failure. Crit Care Med. 1996 Feb;24(2):192–198. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199602000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock M. L., Umen A. J., Finkelstein M., Keane W. F. The assessment of risk factors in 462 patients with acute renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 1985 Feb;5(2):97–103. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(85)80003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chertow G. M., Lazarus J. M., Paganini E. P., Allgren R. L., Lafayette R. A., Sayegh M. H. Predictors of mortality and the provision of dialysis in patients with acute tubular necrosis. The Auriculin Anaritide Acute Renal Failure Study Group. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998 Apr;9(4):692–698. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V94692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druml W., Lax F., Grimm G., Schneeweiss B., Lenz K., Laggner A. N. Acute renal failure in the elderly 1975-1990. Clin Nephrol. 1994 Jun;41(6):342–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVERITT A. V. The urinary excretion of protein, non-protein nitrogen, creatinine and uric acid in ageing male rats. Gerontologia. 1958;2(1):33–46. doi: 10.1159/000210720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feest T. G., Round A., Hamad S. Incidence of severe acute renal failure in adults: results of a community based study. BMJ. 1993 Feb 20;306(6876):481–483. doi: 10.1136/bmj.306.6876.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frocht A., Fillit H. Renal disease in the geriatric patient. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1984 Jan;32(1):28–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1984.tb05148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentric A., Cledes J. Immediate and long-term prognosis in acute renal failure in the elderly. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1991;6(2):86–90. doi: 10.1093/ndt/6.2.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld A. B., Tran D. D., van der Meulen J., Nauta J. J., Thijs L. G. Acute renal failure in the medical intensive care unit: predisposing, complicating factors and outcome. Nephron. 1991;59(4):602–610. doi: 10.1159/000186651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan I. H., Catto G. R., Edward N., Macleod A. M. Acute renal failure: factors influencing nephrology referral and outcome. QJM. 1997 Dec;90(12):781–785. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/90.12.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liaño F., Pascual J. Epidemiology of acute renal failure: a prospective, multicenter, community-based study. Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Kidney Int. 1996 Sep;50(3):811–818. doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindeman R. D., Lee T. D., Jr, Yiengst M. J., Shock N. W. Influence of age, renal disease, hypertension, diuretics, and calcium on the antidiuretic responses to suboptimal infusions of vasopressin. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Aug;68(2):206–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. C., Cook D. J., Christou N. V., Bernard G. R., Sprung C. L., Sibbald W. J. Multiple organ dysfunction score: a reliable descriptor of a complex clinical outcome. Crit Care Med. 1995 Oct;23(10):1638–1652. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199510000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obialo C. I., Okonofua E. C., Nzerue M. C., Tayade A. S., Riley L. J. Role of hypoalbuminemia and hypocholesterolemia as copredictors of mortality in acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1999 Sep;56(3):1058–1063. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00622.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascual J., Liaño F. Causes and prognosis of acute renal failure in the very old. Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1998 Jun;46(6):721–725. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1998.tb03807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascual J., Orofino L., Liaño F., Marcén R., Naya M. T., Orte L., Ortuño J. Incidence and prognosis of acute renal failure in older patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1990 Jan;38(1):25–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1990.tb01592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao T. K., Friedman E. A. Outcome of severe acute renal failure in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995 Mar;25(3):390–398. doi: 10.1016/0272-6386(95)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H. H., Pitt E. A., Ibels L. S., McNeil D. R. Prediction of outcome in acute renal failure by discriminant analysis of clinical variables. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Nov;145(11):2015–2018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder N. A., Feigal D. W., Arieff A. I. Hypernatremia in elderly patients. A heterogeneous, morbid, and iatrogenic entity. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Sep;107(3):309–319. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turney J. H., Marshall D. H., Brownjohn A. M., Ellis C. M., Parsons F. M. The evolution of acute renal failure, 1956-1988. Q J Med. 1990 Jan;74(273):83–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuasa S., Takahashi N., Shoji T., Uchida K., Kiyomoto H., Hashimoto M., Fujioka H., Fujita Y., Hitomi H., Matsuo H. A simple and early prognostic index for acute renal failure patients requiring renal replacement therapy. Artif Organs. 1998 Apr;22(4):273–278. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1594.1998.06025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


