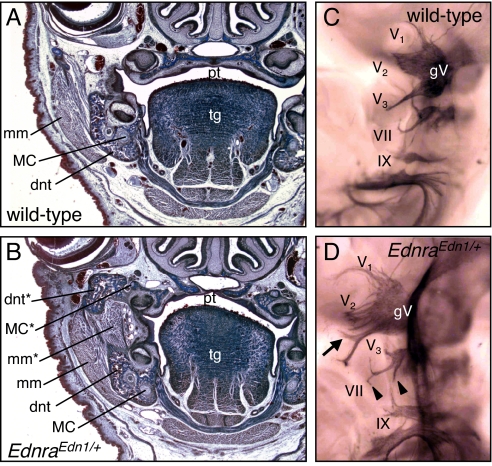
Fig. 3.
Histological and whole-mount neuromuscular analysis of EdnraEdn1/+ mice. (A and B) Frontal sections of E18.5 wild-type (A) and EdnraEdn1/+ (B) mice stained by Mallory trichromic. Constitutive activation of Edn1/Ednra signaling results not only in the transformation of maxillary skeletal elements, but also in the appearance of new muscular components associated to the ectopic dentary, which can be interpreted as a duplicated masseter muscle. (C and D) Cranial nerves of E10.5 wild-type (C) and EdnraEdn1/+ (D) embryos stained by antineurofilament antibody. Ectopic branches of the mandibular (arrow) and facial (arrowheads) nerves are indicated. dnt, dentary; mm, masseter muscle; pl, palatine; tg, tongue; gV, trigeminal ganglion; V1, ophthalmic nerve; V2, maxillary nerve; V1, mandibular nerve; VII, facial nerve; IX, glossopharyngeal nerve; *, ectopic structure.