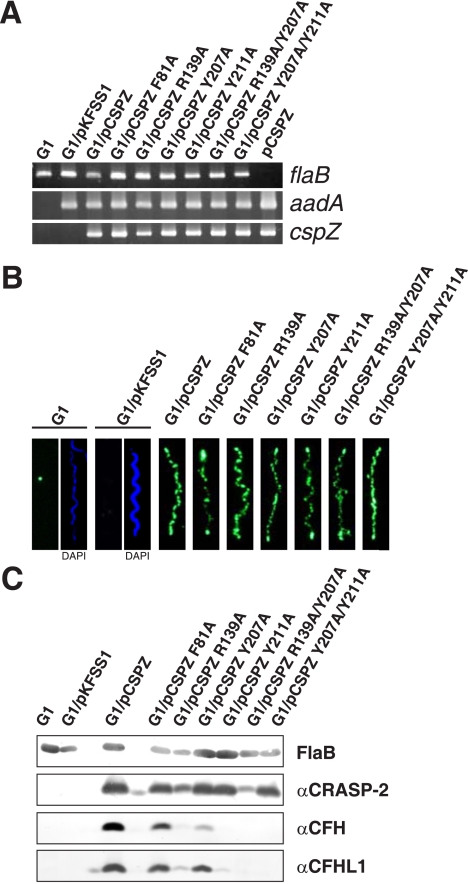
FIGURE 4.
Characterization of B. garinii G1 complemented with BbCRASP-2 and BbCRASP-2 mutants. A, B. garinii G1, G1/pKFSS1, G1/pCSPZ, and G1 strains expressing mutated BbCRASP-2 proteins were characterized by PCR amplification of the flaB, cspZ, and aadA genes using primers listed in supplemental Table S1. B, surface expression of BbCRASP-2 as well as mutated BbCRASP-2 proteins were assessed by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy of intact borrelial cells. Spirochetes were incubated with mouse polyclonal anti-BbCRASP-2 antiserum before fixation. Slides were then incubated with an Alexa 488-conjugated anti-mouse antibody. For counterstaining, the DNA-binding dye 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole were used to identify cells within a given field. For a clearer view only 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole stain of strains G1 and G1/pKFSS1 was presented (right windows of panel 1 and 2). Slides were visualized at a magnification of ×1000. C, expression of BbCRASP-2 proteins in all strains was assessed by ligand affinity blotting. Whole cell lysates were separated by 10% Tris/Tricine-SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. The membranes were incubated with either purified CFHL1 or NHS, and binding of proteins was detected with the indicated antisera, e.g. polyclonal rabbit αSCR1–4 antiserum specific to CFHL1 and monoclonal antibody VIG8 specific for SCR20 of CFH. A monoclonal antibody, L41 1C11, specific for the flagellin protein, FlaB, was used to show similar loading of the borrelial cell lysates.