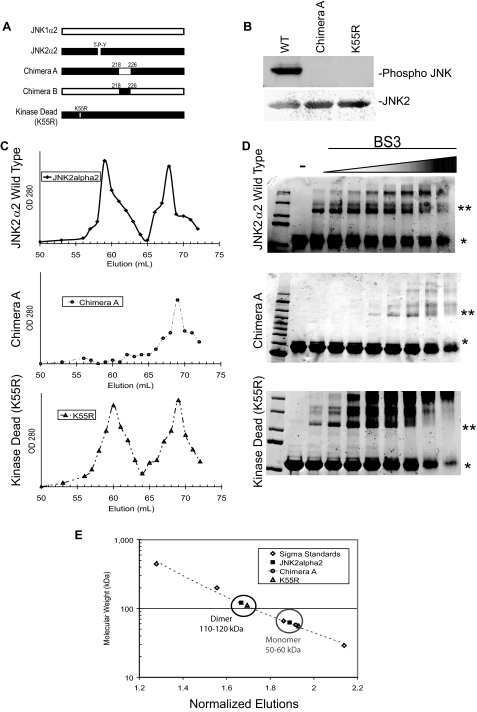
FIGURE 2.
JNK2α2 dimerization in vitro is dependent on the α-region and is independent of phosphorylation. A, schematic of JNK2α2 chimeras and mutants. JNK1α2 and JNK2α2 sequences are indicated by white bars and black bars, respectively. The α-region is defined as the amino acids 218–226. The kinase dead JNK2α2 mutation (K55R) and the position of the T-P-Y motif are also shown. B, in vitro kinase reactions with purified JNK2α2 constructs. Western analysis using an antibody specific for phosphorylated T-P-Y in JNK (top panel) or JNK2 (bottom panel). WT, wild type JNK2α2. K55R, kinase dead mutant. C, gel filtration of JNK2α2 wild type and JNK mutants. JNK2α2 wild type (top panel), Chimera A (middle panel), and kinase dead mutant-K55R (bottom panel) were applied to a Sephacryl S-400 gel filtration column. 1-ml fractions were collected, and the A280 nm value was measured. D, cross-linking analysis of purified JNK2α2 protein was incubated with increasing concentrations of the homo-bifunctional cross-linker BS3. The samples were analyzed using SDS-PAGE and then stained with Coomassie Blue. -, samples not treated with BS3. * indicates the JNK2α2 monomer. ** indicates the JNK2α2 dimer. E, Sigma Protein Standards were applied to the gel filtration column to generate a standard curve in which the molecular mass of each standard protein was plotted against its normalized fraction (see “Experimental Procedures”). The black circle indicates fractions that are ∼110–120 kDa (dimer), and the gray circle shows fractions that are ∼50–60 kDa (monomer).