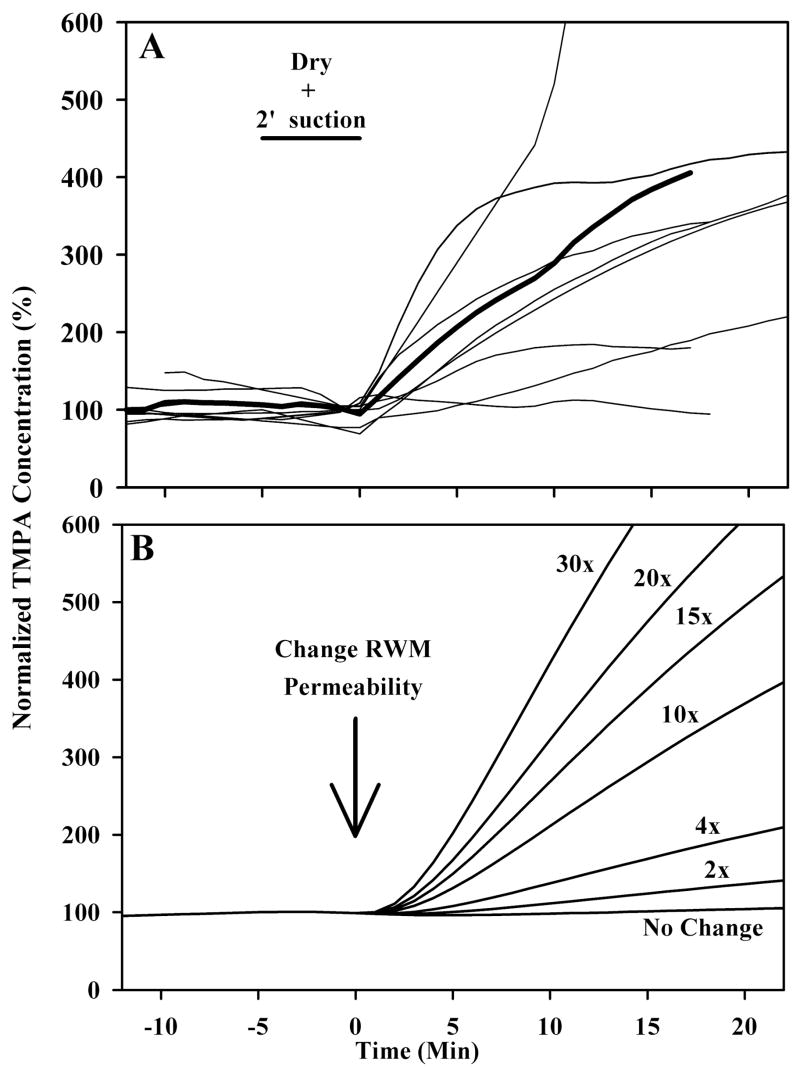
Figure 5.
In panel A, light traces show individual experiments in which the round window membrane was exposed to either control or permeability-altering treatments. Solution was removed from the bulla and suction was applied to the round window niche for 2 minutes, and then TMPA containing solution was reapplied to the bulla. The mean is shown by the dark line. In panel B, a finite-element model was used to calculate entry rates with varying degrees of round window membrane permeability change. By comparison with the measured curves in panel A, it is estimated that drying due to suction increases round window membrane permeability by a factor of 3 to 5 times and high osmolarity by a factor of 10 to 15 times.