Table 2.
Identification of Optimal Chiral Ligand and Proton Source for the conversion of 5a to 6a.
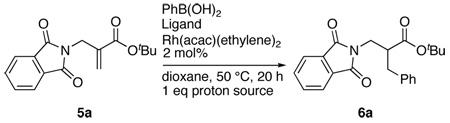 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | ligand | proton sourcea | yield, (SM) %b | ee, %c |
| 1 | (S)-BINAP | 2-Methoxyphenol | 31 (49) | 81 |
| 2 | (S)-BINAP | 2-Acetylphenol | 84 (2) | 77 |
| 3 | (S)-BINAP | Phthalimide | 56 (34) | 82 |
| 4 | (S)-Tol-BINAP | 2-Methoxyphenol | 21 (39) | 73 |
| 5 | (S)-Tol-BINAP | 2-Acetylphenol | 42 (40) | 77 |
| 6 | (S,S)-DIOP | 2-Methoxyphenol | 43 (31) | 36 |
| 7 | (R,R)-CHIRAPHOS | 2-Methoxyphenol | 8 (80) | nd |
| 8 | (R,S)-JOSIPHOS | 2-Methoxyphenol | 0 (95) | - |
| 9 | (S)-MethylBOPhoz | 2-Methoxyphenol | 8 (87) | nd |
| 10 | (S)-SYNPHOS | 2-Methoxyphenol | 1 (73) | nd |
| 11 | (S)-SYNPHOS | 2-Acetylphenol | 30 (67) | 71 |
| 12 | (S)-SYNPHOS | Phthalimide | 25 (50) | 70 |
| 13 | (S)-DIFLUORPHOS | 2-Methoxyphenol | 8 (83) | nd |
| 14 | (S)-DIFLUORPHOS | 2-Acetylphenol | 71 (15) | 88 |
| 15 | (S)-DIFLUORPHOS | Phthalimide | 91 (0) | 88 |
One equivalent of the proton source was used. The reactions were carried out at 50 °C using dioxane as a solvent and 2 mol% of the chiral rhodium catalyst.
Isolated yields. Yields in parenthesis are for recovered starting materials.
Chiral HPLC analysis; nd = not determined.
