Figure 4. BIBW 2992 more potently inhibits both sensitive and resistant EGFR mutants, including T854A.
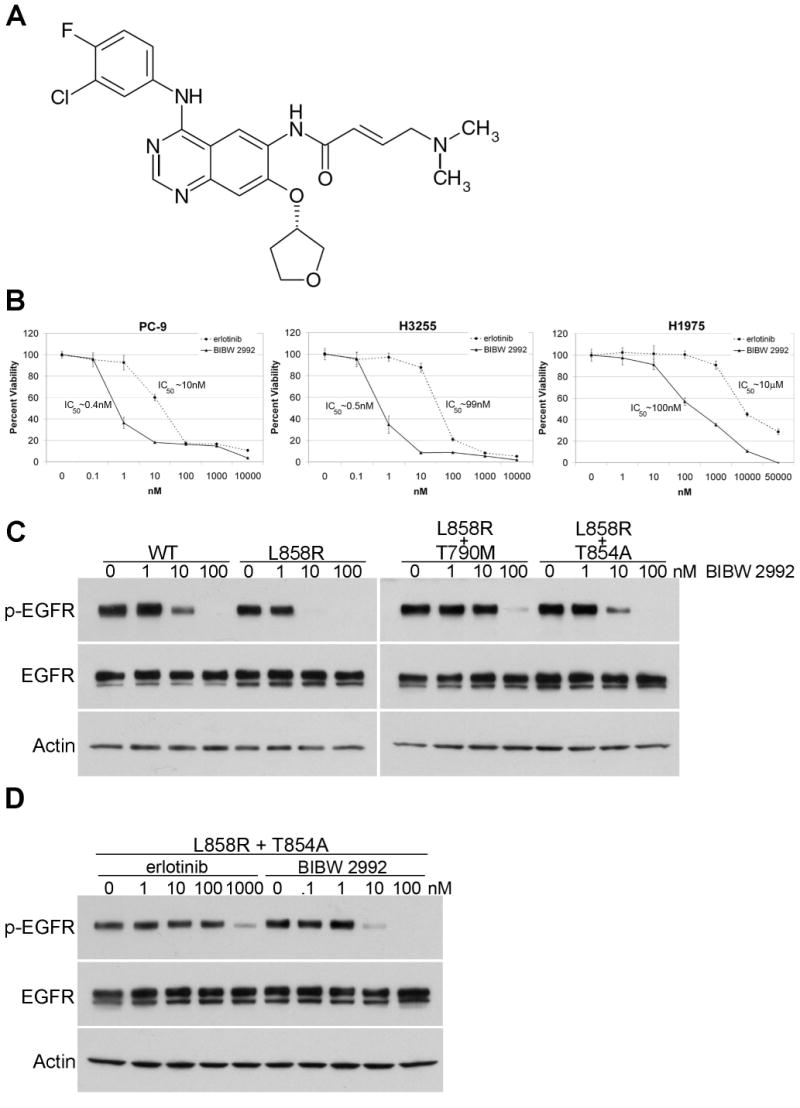
A) Chemical structure of BIBW 2992. Adapted from (21). B) Cell growth inhibition assays of three EGFR mutant cell lines treated with various does of erlotinib (dashed line) or BIBW 2992 (solid line). PC-9 cells have a drug-sensitive exon 19 deletion in EGFR, H3255 cells have the drug-sensitive L858R mutation, and H1975 cells have both L858R and the T790M resistance mutation. All plots are relative to a DMSO-only control and error bars indicate one standard deviation from six replicates. All assays were performed three independent times and representative plots are shown. IC50 values were calculated using BioDataFit 1.02. C) Lysates from 293T cells transiently transfected with cDNAs encoding either EGFR WT, L858R, L858R plus T790M, or L858R plus T854A and treated with different concentrations of BIBW 2992 were immunoblotted for phospho-EGFR, total EGFR, and actin. Actin is shown as a loading control. D) Lysates from 293T cells transiently transfected with L858R plus T854A EGFR cDNA and treated with different concentrations of erlotinib or BIBW 2992 were immunoblotted for phospho-EGFR, total EGFR, and actin.
