Fig. 3.
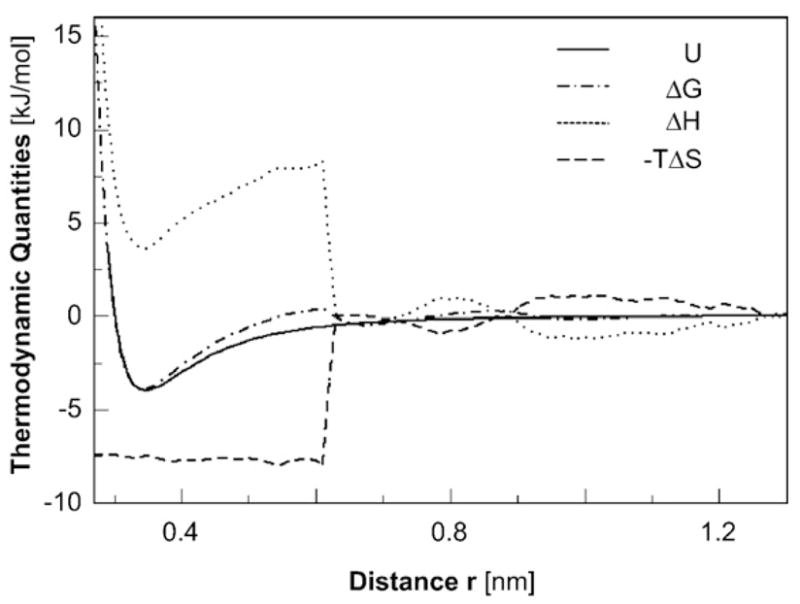
Interactions between idealized hydrophobic surfaces. Two graphene carbon surfaces of 60 atoms each are brought together in water via free-energy simulations.55 Plotted as a function of the plate-to-plate separation r and normalized to represent the contribution per atom in the surfaces are the changes in energy U, the free energy ΔG, the enthalpy ΔH, and the entropic contribution −TΔS.
