Figure 2.
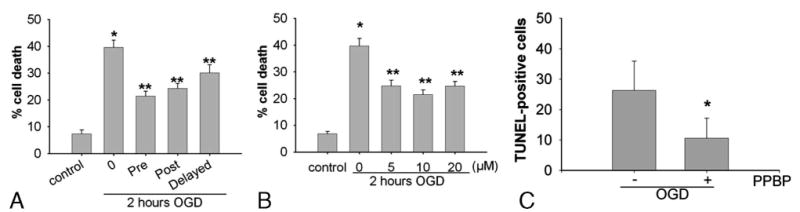
A. Protective effects of 4-phenyl-1-(4-phenylbutyl) piperidine (PPBP) against oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced neuronal injury. After 2 h of OGD, treatment with 5,10, and 20 μM PPBP treatment initiated 15 min before OGD and continued for 24 h postreoxygenation reduced neuronal death. *P < 0.05 versus control and **P < 0.05 vs. 2 h OGD (n = 5). B. Protection conferred by pretreatment and posttreatment after 2 h of oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD) followed by reoxygenation. Neuronal death was decreased by PPBP pretreatment (10 μM, initiated 15 min before OGD), early posttreatment (10 μM, initiated 15 min after reoxygenation) or delayed posttreatment (10 μM, initiated 1 h after reoxygenation). Cell death was assessed 24 h after OGD (n = 5). *P < 0.05 versus control and **P < 0.05 versus 2 h OGD. C. Effect of PPBP treatment with OGD on TUNEL-positive cells. *P < 0.05 versus without OGD treatment.
