Fig. 5.
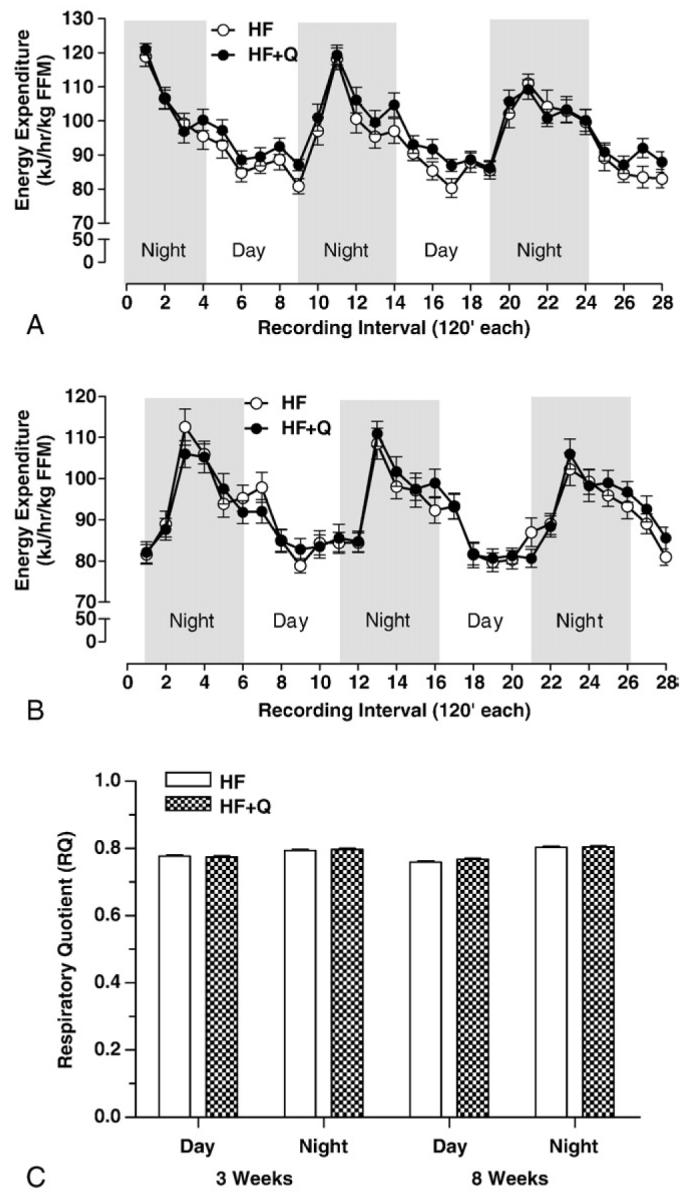
Energy expenditure (kilojoules per hour per FFM) was measured by indirect calorimetry in mice after 3W (A) or 8W (B) on the respective HF (n = 8) or HF + Q (n = 8) diets. Mean EEs during the night and day intervals were compared between diets at 3 and 8W using 2-way ANOVA as described in Methods. Mean EE during the night at 3W and during the day and night at 8W did not differ between dietary groups, but mean EE during the day at 3W was significantly higher (P < .05) in the HF + Q compared with the HF group. (C) Oxygen consumption and CO2 production were measured continuously at 45-minute intervals for 3 days by indirect calorimetry in mice after 3 and 8W on the respective HF (n = 8) or HF + Q (n = 8) diets. Respiratory quotients were calculated as the ratio of CO2 produced vs O2 consumed, and mean RQs were obtained from the measurements taken between 7:00 pm and 7:00 am (night) and between 7:00 am and 7:00 pm (day). Mean day and night RQs determined after 3 and 8W on the respective diets were compared using 2-way ANOVA as described in Methods. Mean RQs did not differ between diets and between time of day, and no time of day × diet interaction was detected.
