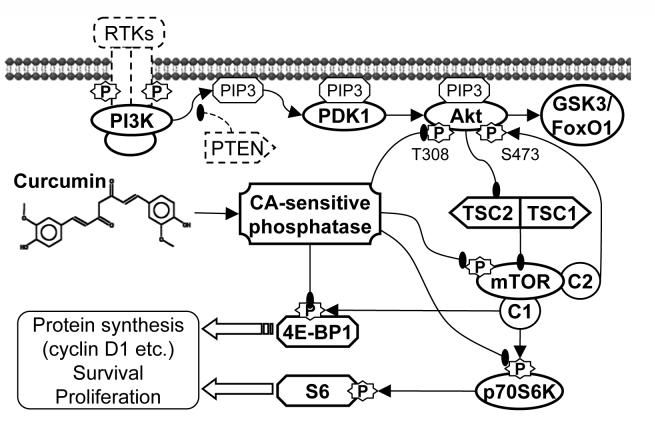
Figure 7.
Summary of the mechanisms by which curcumin inhibits Akt/mTOR signaling and cell survival/proliferation in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Curcumin activated PP2A and/or unspecified calyculin A-sensitive protein phosphatase activities towards Akt, mTOR, led to the dephosphorylation of Akt/mTOR and their downstream substrates GSK3, FoxO1, p70S6K and 4E-BP1, and finally inhibited the expression of proteins that are essential for cell survival and proliferation. Curcumin also activated MAPKs and AMPK; however these kinases did not play important roles in the curcumin-mediated inhibition of Akt/mTOR signaling and cell proliferation.