Fig. 3.
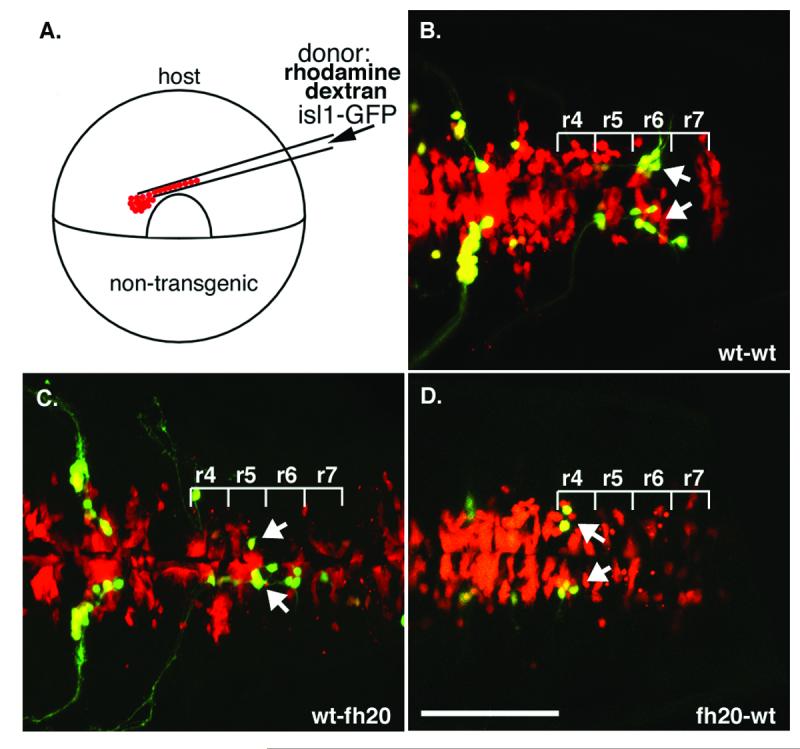
foggy/spt5 is required cell-autonomously for facial branchiomotor neuron migration. (A) Genetic mosaics were generated by transplanting cells from rhodamine dextran-labeled isl1-GFP transgenic donor cells to unlabeled hosts at gastrula stage (6 hpf), and confocal images were collected at 36 hpf. Donor-derived cells are red, and donor derived motor neurons, which express GFP, are yellow. (B) Wild-type facial motor neurons (arrow) migrate posteriorly in a wild-type host; n=14/14. (C) Wild-type facial motor neurons (arrows) also migrate posteriorly from r4 in a foggy/spt5fh20 mutant host, though to a lesser extent than in wild-type to wild-type control mosaics; n=14/20. (D) foggy/spt5fh20 facial motor neurons (arrow) fail to migrate from r4 in a wild-type host; n=11/11. Scalebar = 100μm.
