Fig. 4.
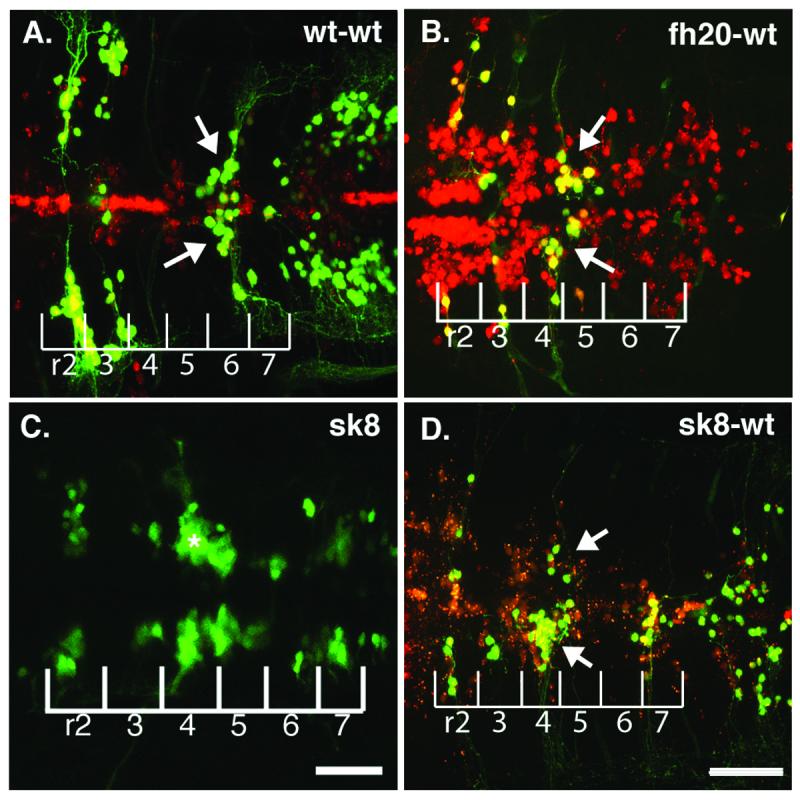
spt5 is not required for facial branchiomotor neuron survival to at least 5 dpf (A) wild-type transplant hosts containing wild-type donor cells (red) and donor-derived motor neurons (yellow) at 5 dpf. Wild-type facial motor neurons (arrow) in a wild-type host migrate posteriorly, differentiate and extend normal axonal processes from r4. (B) Hypomorphic foggy/spt5fh20 facial motor neurons (arrow) placed in a wild-type host fail to migrate but are still detectable by GFP expression and have normal morphology with axons extending from r4 at 5 dpf; n=12/13. (C) The isl1-GFP motor neuron phenotype of the foggy/spt5sk8 null allele at 48 hpf demonstrates that facial motor neurons fail to migrate posteriorly from r4 (asterisk). (D) foggy/spt5sk8 null facial motor neurons (arrow) placed in a wild-type host fail to migrate normally but have axons extending from r4 at 5 dpf; n=8/8. Scalebars = 40μm. Scalebar in D also corresponds with A and B.
