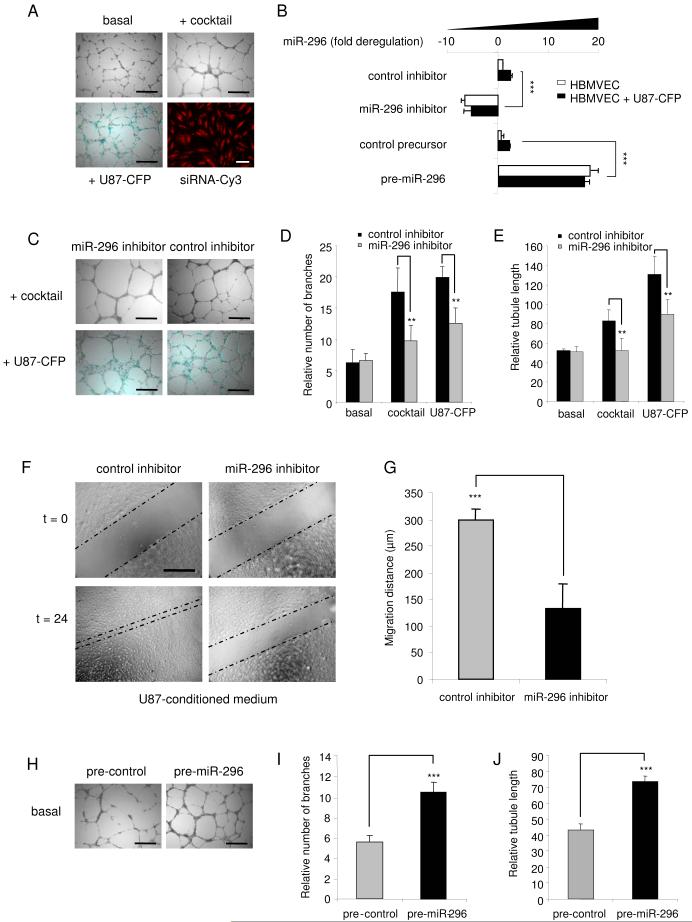
Fig. 3.
Angiogenesis co-culture assay: miR-296-mediated inhibition and induction of angiogenesis (A) HBMVECs cells were cultured on Matrigel-coated plates in basal medium (EBM; Cambrex) only, or basal medium supplemented with a cocktail of angiogenic factors (EGM), or with U87-CFP cells [size bar 300 μm]. Transfection efficiency of endothelial cells was determined (>99%) by using siRNA-Cy3 molecules [monolayer culture, size bar 50 μm]. (B) HBMVECs were transfected with anti-miR-296 inhibitor, pre-miR-296, or non-related control molecules and cultured in the presence or absence of U87-CFP cells. Inhibition and overexpression of miR-296 in CD31+-isolated endothelial cells was quantified by qRT-PCR. (C) HBMVECs were transfected with anti-miR-296 inhibitor or non-related control molecules and analyzed for tubule formation, size bar 300 μm. (D and E) Tubule formation was evaluated at 48 hr after transfection including 24 hr of culturing on Matrigel using the imaging program Image J. A significant decrease in tubule branching (D) and tubule length (E) was observed after transfection with the miR-296 inhibitor. (F) HBMVECs were transfected with anti-miR-296 inhibitor or non-related control molecules and analyzed for migration capacity. Inhibition of miR-296 resulted in a significant decrease in migration, as quantified in (G). (H) Overexpression of miR-296 at 24 hr after transfection of pre-miR-296 molecules resulted in increased angiogenesis in vitro [size bar 300 μm], as quantified by measuring tubule branching (I) and tubule length (J). Error bars indicate S.D., **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, t test.