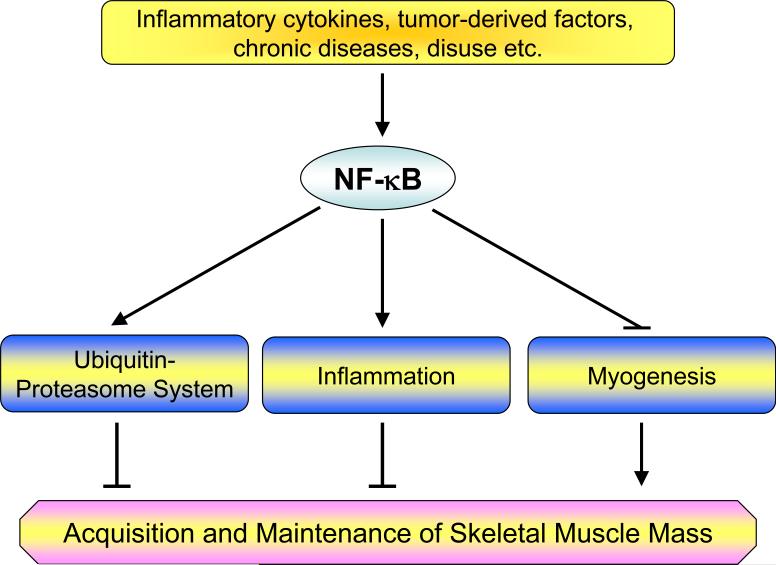
Figure 3. Putative mechanisms of action of NF-κB in skeletal muscle metabolism.
Activation of NF-κB leads to muscle-wasting by multiple mechanisms. NF-κB can augment the expression of ubiquitin-proteasome system proteins (e.g. MURF1) and/or proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and tissue-degrading enzymes which leads to skeletal muscle-wasting. Activation of NF-κB can also induce muscle-wasting by blocking the process of myogenic differentiation possibly by modulating the levels of MyoD.