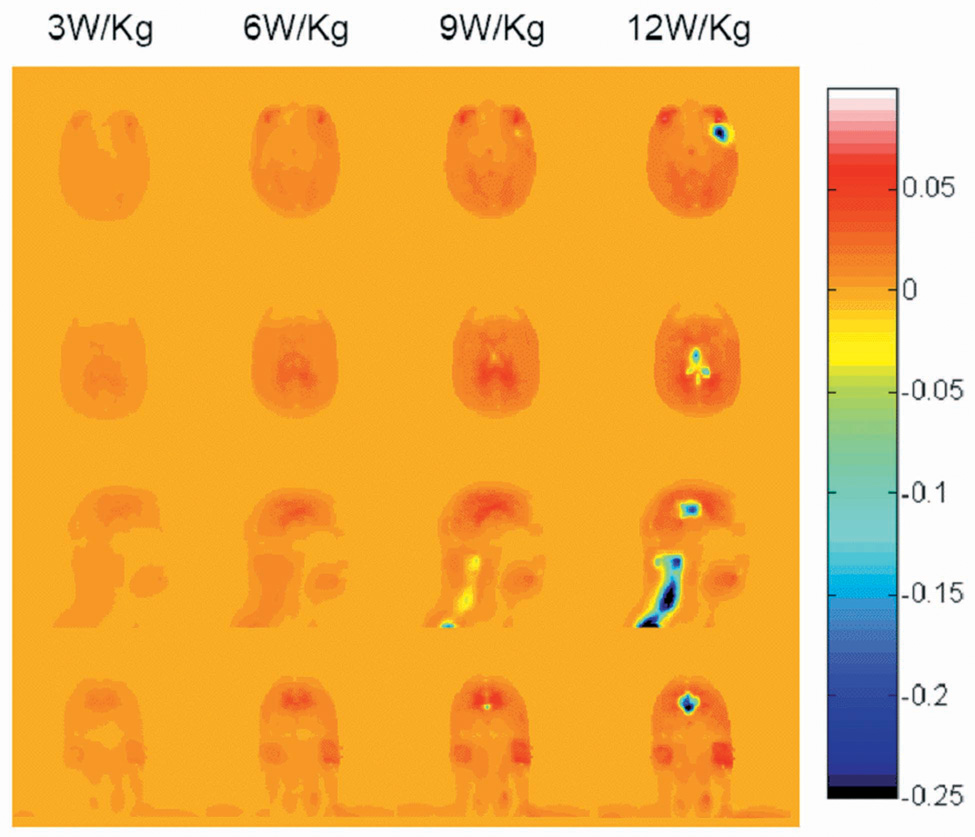
Fig. 2.
Calculated difference in Temperature increase (°C) with and without consideration of physiological response (with minus without) for a human head in a volume coil for 30 minutes at 300 MHz with a head-average SAR of 3.0 W/kg, 6.0 W/kg, 9.0 W/kg and 12.0 W/kg (left to right) on an axial plane passing through the eyes (top), an axial plane passing through the center of the coil and brain (2nd row), and sagittal and coronal planes passing through the center of the coil and brain (3rd and bottom rows). Positive values generally occur where slight temperature increases cause small increases in metabolic rate, but where the temperature does not exceed 39°C enough to cause a significant thermoreglatory increase in perfusion. Negative values occur where thermoregulatory increases in perfusion have a notable effect.