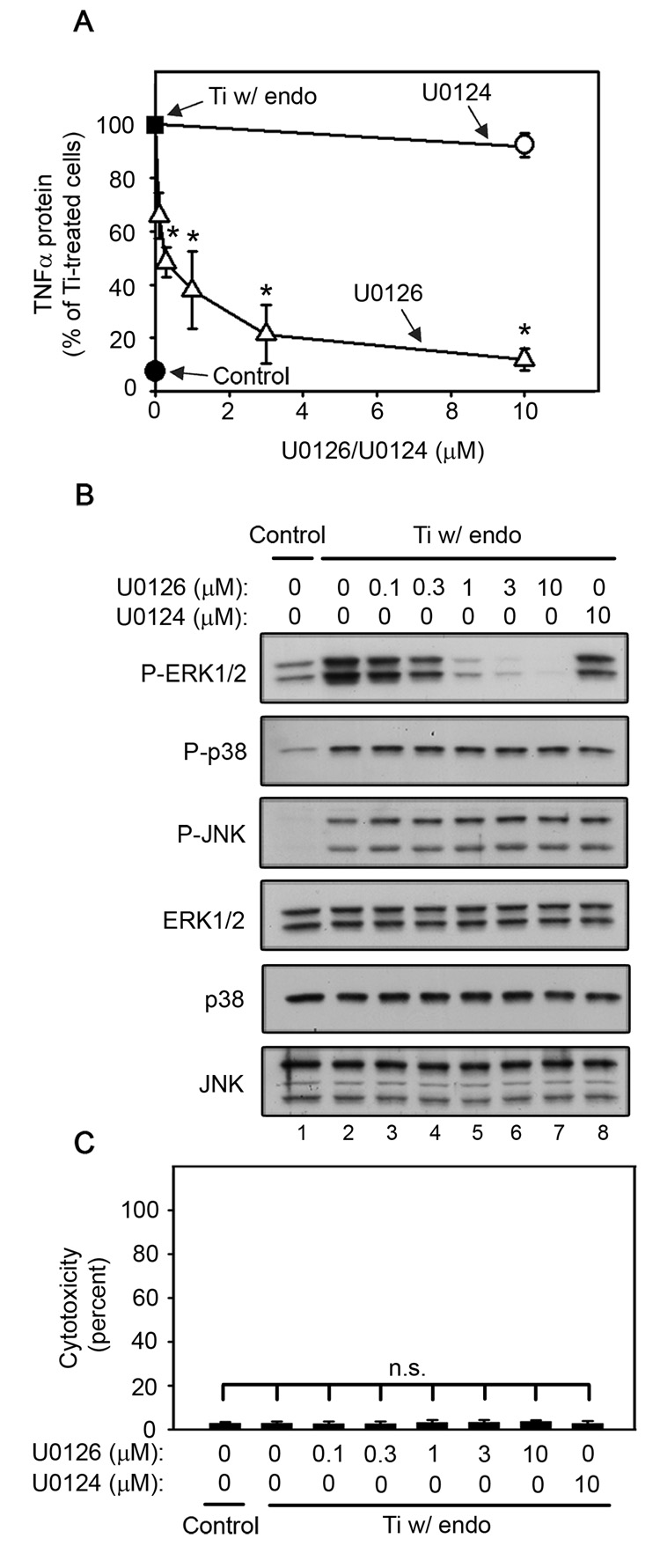
Fig. 2.
ERK1/2 activation is required for titanium particle-induced TNFα production by RAW264.7 macrophages since U0126 dose-dependently inhibits TNFα production (A) and ERK1/2 phosphorylation (B), but does not induce cytotoxicity (C) following stimulation by titanium particles with adherent endotoxin. All groups received a mixture of vehicle controls, such that all contained 0.04% PBS and 0.1% DMSO. (A) TNFα protein was measured in conditioned media by ELISA following stimulation for 90 minutes with titanium particles with adherent endotoxin in the presence of indicated concentrations of U0126 (open triangles) or U0124 (open circle), or in the absence of both (closed square). TNFα protein was also measured in conditioned media collected following culture without titanium particles or inhibitor (closed circle). Results (mean ±SEM of four experiments) are presented as a percentage of TNFα protein following stimulation with titanium particles with adherent endotoxin in the absence of inhibitors (closed square). Asterisks denote p<0.005 compared to the control group (closed square) and the group with the relatively inactive analogue (open circle). (B) MAPK activation was assessed in whole cell lysates as described in Figure 1B. Western blots are from the most representative of the four experiments pooled in (A). (C) Cytotoxicity results are presented as the mean ± SEM of the four experiments pooled in (A).