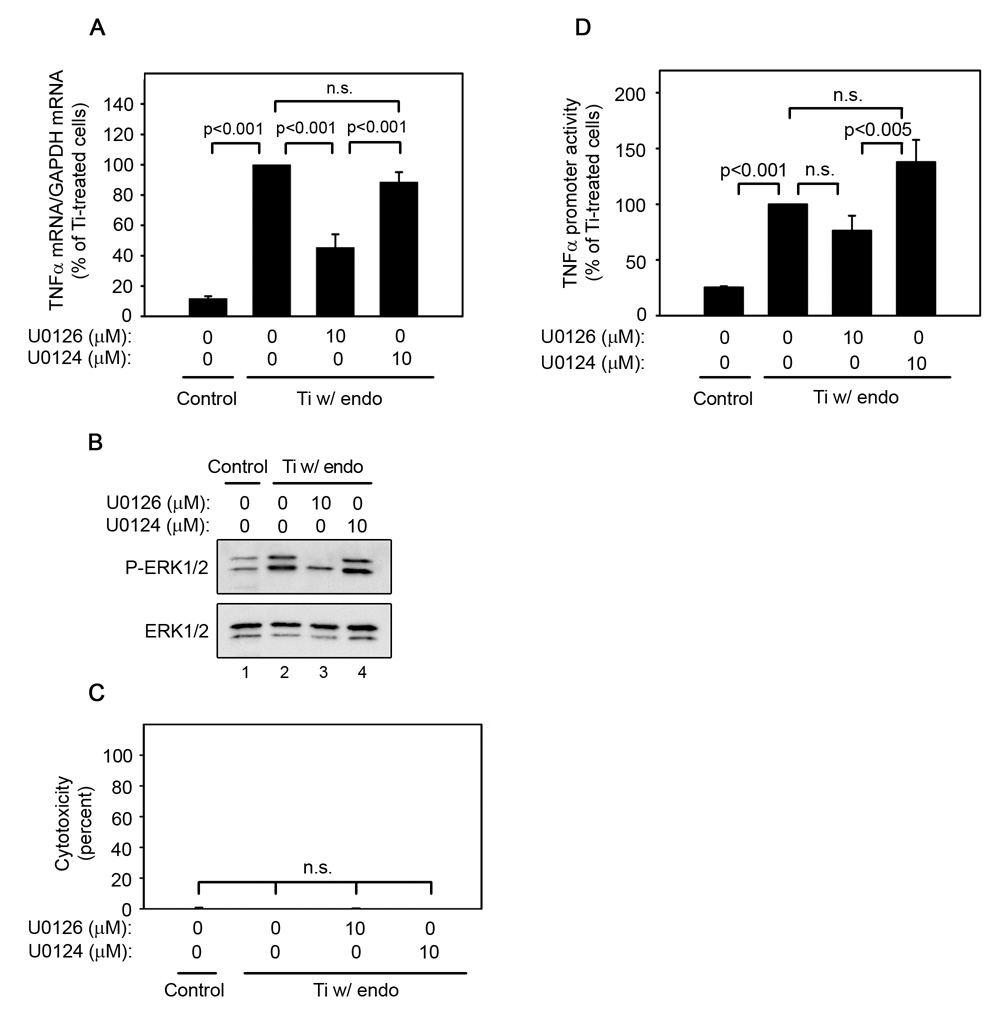
Fig. 4.
ERK1/2 activation is required for titanium particle-induced TNFα mRNA expression and promoter activity since U0126 inhibits TNFα mRNA (A), promoter activity (D), and ERK1/2 phosphorylation (B), but does not induce cytotoxicity (C) following stimulation by titanium particles with adherent endotoxin. All groups received a mixture of vehicle controls, such that all contained 0.04% PBS and 0.1% DMSO. (A) TNFα mRNA was measured by real-time PCR following stimulation of bone marrow-derived macrophages for 30 minutes with or without titanium particles with adherent endotoxin in the presence or absence of indicated concentrations of U0126 or U0124. Results (mean ± SEM of four experiments) are presented as a percentage of TNFα mRNA following stimulation with titanium particles with adherent endotoxin in the absence of inhibitors. (B) MAPK activation was assessed in whole cell lysates as described in Figure 1B. Western blots are from the most representative of the four experiments pooled in (A). (C) Cytotoxicity results are presented as the mean ± SEM of the four experiments pooled in (A). (D) TNFα promoter activity was measured using a luciferase reporter construct following stimulation of RAW264.7 cells with or without titanium particles with adherent endotoxin in the presence or absence of U0126 or U0124 for 4 hours. Results (mean ± SEM of eight experiments) are presented as a percentage of promoter activity following stimulation with titanium particles with adherent endotoxin in the absence of inhibitors.