Figure 5. Deletion of PDR1 enhances the sensitivity of pdr1DBD-repressor fusions to etoposide.
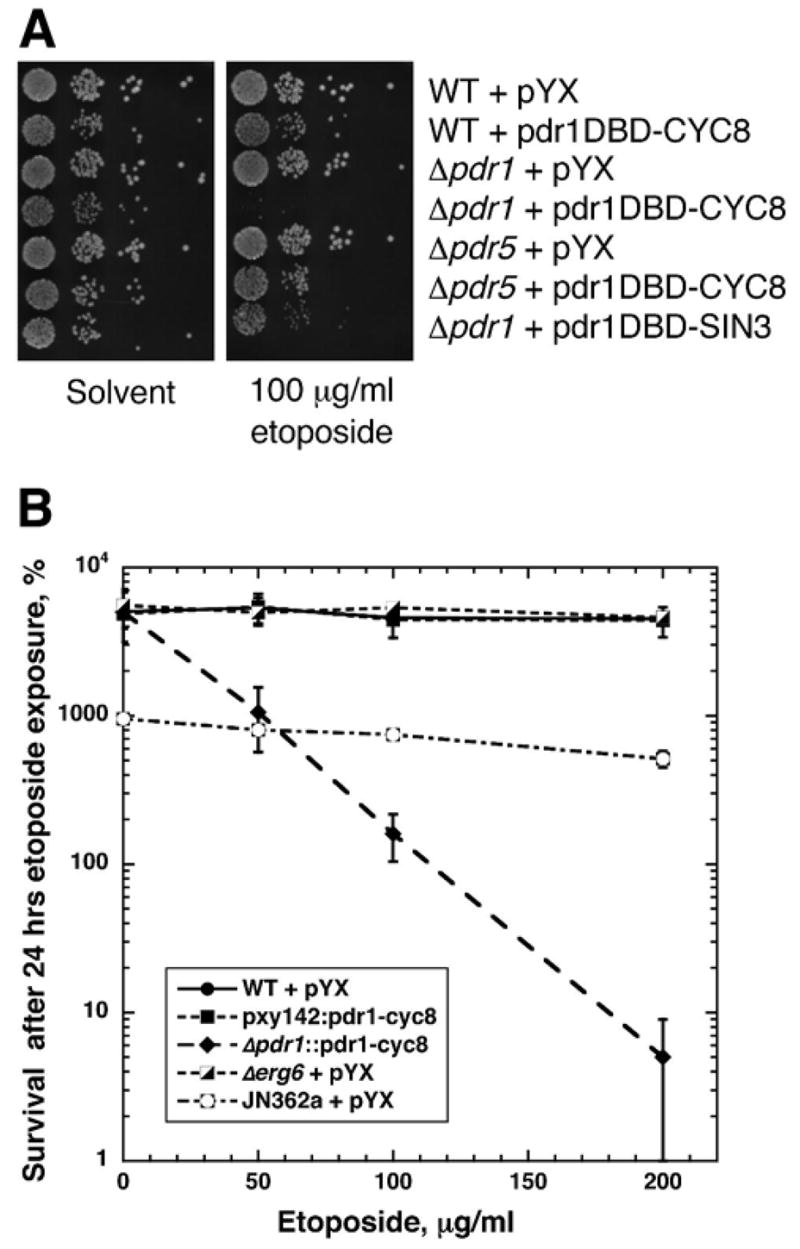
(a) Cell sensitivity was carried out similar to the experiments shown in Figure 1a using either a solvent control or 100 μg/ml etoposide containing media. The strains used are indicated on the figure. The results of this experiment show that deletion of either PDR1 or PDR5 alone is insufficient to confer etoposide sensitivity, and that strong synergistic sensitivity is seen with pdr1DBD-CYC8 and deletion of PDR1 but not deletion of PDR5. For etoposide, pdr1DBD-CYC8 appears superior to pdr1DBD-SIN3. (b) Clonogenic surival assays were carried out using the strains indicated in the legend. Cells were treated in SD-leu medium containing indicated concentrations of etoposide for 24 hrs. After incubation, aliquots were removed, diluted, and plated to SD-leu plates to determine viable titer. WT cells were strain BY4741, and all strains shown (except JN362a are BY4741 derivatives. Survival is shown relative to the viable titer at the time of etoposide addition. Cytotoxicity is indicated in this experiment by a viability below 100%.
