Figure 3.
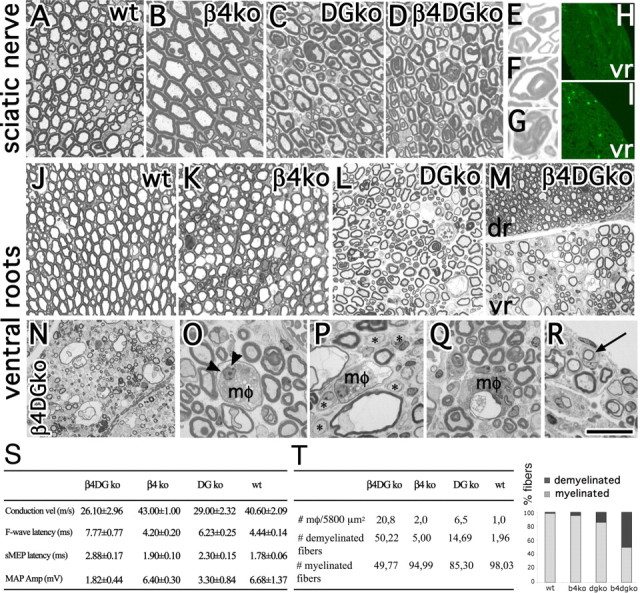
Excessive myelin folding in sciatic nerves, with myelin breakdown and degeneration in roots of double-mutant mice. A–M, Transversal semithin sections from 12-month-old sciatic nerves and ventral roots. A–G, Both DG-null and double-mutant nerves contain abnormal loops (e.g., in E), infoldings (e.g., in F), and outfoldings (e.g., in G). J–M, Ventral roots lacking dystroglycan (L) show hypomyelination. M–T, Hypomyelination in double-mutant mice is severe in ventral [M (vr), N], but not dorsal (dr) roots, with signs of acute demyelination including macrophages (mφ) engulfing degenerated axons (O, arrowheads) and myelin breakdown products (O, P, Q, mφ), thin myelin sheaths (P), and demyelinated axons (P, asterisks). R, Signs of remyelination (onion bulbs, arrow) are present. H, I, Staining with anti-CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1) antibodies reveals the presence of macrophages infiltrating double-mutant (I) but rarely wild-type (wt; H) roots. T, The number of demyelinated axons was significantly higher in double- than dystroglycan single-mutant mice (p < 0.001 by Student's t test; n = 4 DG-null and 6 double-null mice). Macrophage infiltration was higher in double mutants than in DG-null mice (p < 0.001 by Student's t test; n = 6 DG-null mice, 6 double-mutant mice). S, Neurophysiology in 12-month-old β4 integrin/DG-null mice and controls confirms that DG-null mice have a neuropathy with reduced nerve conduction velocity (vel) and increased latencies of motor-evoked potential (sMEP) and of F-wave. These parameters worsen in double-mutant mice, although the differences do not reach statistical significance. The reduction in motor action potential (MAP) amplitude (Amp) became statistically different in double mutants compared with wt mice (p = 0.044 by paired t test; n = 6 double-null, 2 β4 integrin-null, 4 DG-null, 5 wt). Values and SEMs are indicated for each genotype. Scale bar: (in R) A–D, 30 μm; E–G, 11.5 μm; J–M, 50 μm; N–R, 25 μm.
