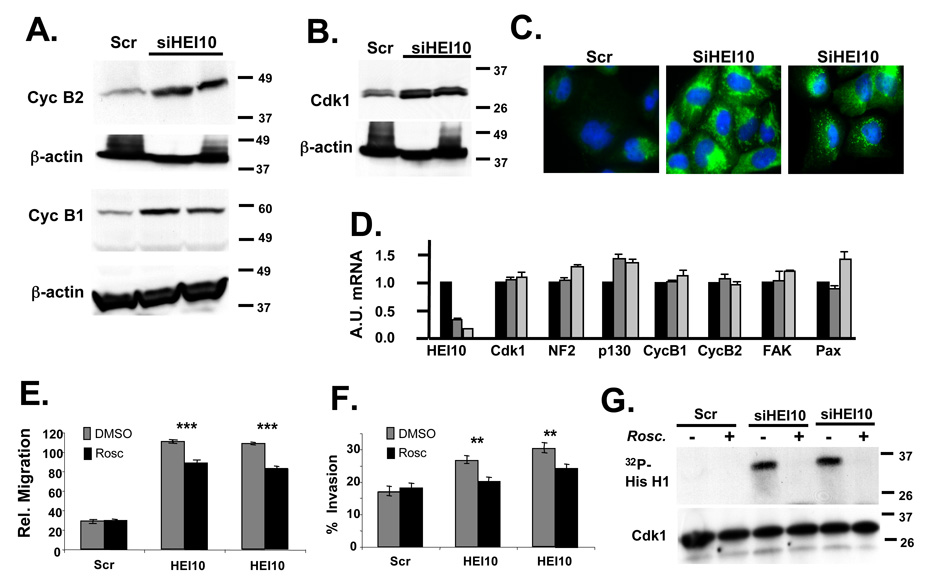
Figure 5. HEI10 depletion induces Cdk1 and B-type cyclins to increase migration and invasion.
A Experiment as in 4A. Antibodies used for initial probe were to cyclin B1 and cyclin B2, as indicated; all blots were stripped and reprobed with antibody to β-actin. B. Experiment as in 4A. Antibodies used for initial probe were to Cdk1. C. Immunofluorescence of U2OS treated with Scr siRNA or two different HEI10-directed siRNAs, visualized with antibodies to cyclin B2 (green). DNA is stained with DAPI (blue). D. RT-qPCR analysis. Total RNA was prepared in parallel to the protein lysates analyzed in the experiments in Figure 4 and Figure 5. A.U., Arbitrary Units used to describe relative abundance of each mRNA listed. E, F. U2OS cells were treated with Scr- or two different HEI10-directed siRNAs in the presence of DMSO vehicle (negative control) or the Cdk1 inhibitor roscovitine. Migration (E) and invasion (F) were assayed as described in Figure 2 and Figure 3. Degree of significance of roscovitine reversal of phenotypes is P ***<0.0001 for migration (E) and **P < 0.005 for invasion (F). G. Cdk1 was immunoprecipitated with antibody to Cdk1 from cells treated as in E, and Cdk1-kinase activity assayed. Top panel shows 32P-labeled histone H1 substrate phoshorylated by Cdk1/cycB; bottom panel, total level of immunoprecipitated Cdk1.