Figure 4.
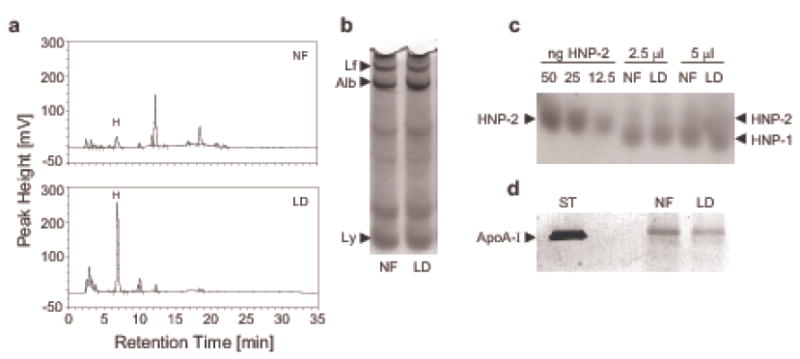
Non-polar lipids can be selectively removed from nasal fluid by solid-phase extraction. Nasal fluid was pooled from three donors (D1, D2, and D3) and subjected to solid phase extraction using a tC18 Sep-Pak cartridge to selectively remove less polar lipids. Aliquots from nasal fluid (NF) and lipid-depleted nasal fluid (LD) were adjusted to the same protein concentration and analyzed by rpHPLC/ELSD (a); silverstained AU-PAGE (b); Western immunoblotting probing for human neutrophil peptides HNP1-3 (c) and apolipoprotein apoA-I (d). (a) rpHPLC/ELSD Chromatograms of lipid extracts from 200 μl of NF and LD each; H: heptadecanoic acid (C17:0). In this example an overall lipid reduction of 89.5 % was achieved. (b) 2 μl of NF and LD were loaded, Lf: lactoferrin, Alb: albumin, Ly: lysozyme. (c) Samples were probed with a polyclonal rabbit antiserum against HNP1-3 and HNP-specific bands were visualized with an alkaline phosphatase/BCIP/NBT detection system; (d) 2 μl of serum standard (ST) and 25 μl of NF and LD each were probed for apo-AI.
