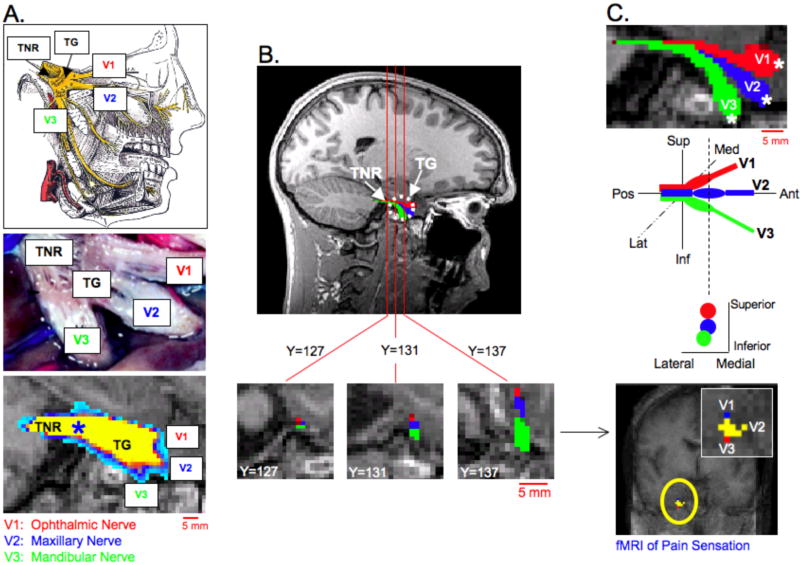
Figure 2. Peripheral Branches of Trigeminal System I.
A. Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve Root (TNR), Trigeminal Ganglion (TG) and division of the peripheral trigeminal nerve branches. The three peripheral branches include V1 (ophthalmic nerve), V2 (maxillary nerve) and V3 (mandibular nerve). The top image in A. depicts the divisions of the trigeminal nerve at the level of the TG as well as the complete peripheral pathways of V1, V2 and V3 (25), while the middle image in A. was adopted from a histological investigation of the peripheral human trigeminal system by Williams et al. (24). The bottom image in A. was obtained by placing a seeding mask in the TNR (blue asterisk) and performing probabilistic tractography (Subject 1, See also Segmentation 1 in Methods and Materials). All possible pathways through the seed regions were identified (waypoints not implemented). The TG was identified along with a division of three peripheral pathways within the TG. B. Using the initial tractography results shown in A. three seeding masks (white asterisks) were placed in the general regions of V1, V2 and V3 near the TG. Coronal slices are shown through the TNR and TG. A clear division of the three trigeminal nerve branches can be seen at the level of the TG (Y=137), but not in the TNR (Y=127). (Each coronal slice is of 1mm slice thickness and in native T1-weighted anatomical space.) The latter probabilistic tractography results depicted a segmentation of the three trigeminal nerve branches, within the TG. C. An enlarged sagittal view of the three branches is shown in the top image. The differentiation of V1, V2 and V3 correlated well with previous functional imaging findings in the TG (2).