Fig 1.
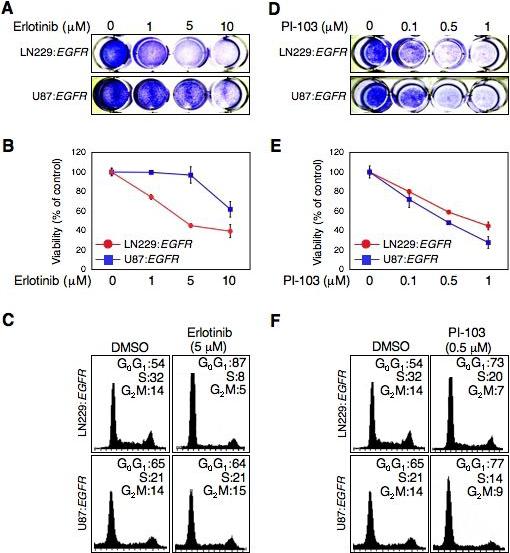
EGFR inhibitor erlotinib inhibits cell proliferation and induces G0G1 arrest dependent on PTEN status. In contrast, anti-proliferative effects of the dual PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor PI-103 were not dependent on PTEN status. LN229:EGFR (PTENwt) and U87:EGFR (PTENmt) cells were treated with erlotinib or PI-103. (A and D) Cell proliferation was visualized by crystal-violet staining of cells after treatment with erlotnib or PI-103 for 72h at dosages indicated. (B and E) Cell growth was determined using WST-1 assay after treatment with erlotinib or PI-103 for 72h at dosages indicated. Error between triplicate measurements for each value shown. (C and F) Cells were treated with erlotinib 5 μM or PI-103 0.5 μM for 24 hr. Cells were trypsinized and prepared for flow cytometric analysis of cell cycle distribution. Percentage of cells in G0G1, S, and G2M phases of the cell cycle is indicated.
