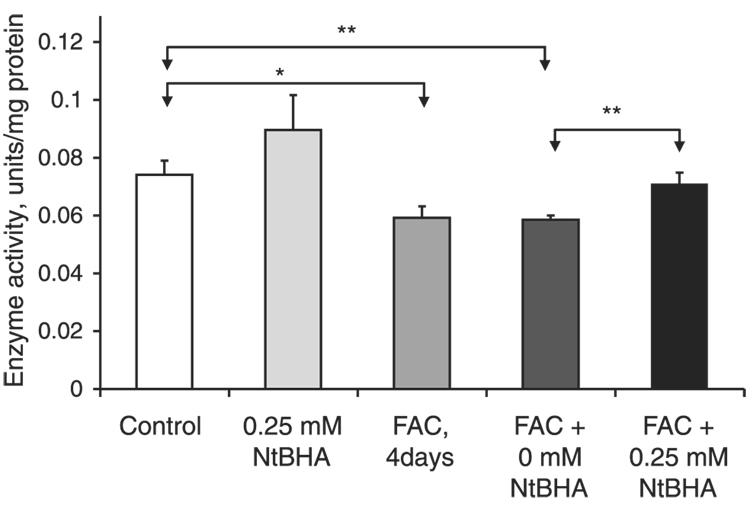
Figure 6.
Effect of iron overload and NtBHA treatment on mitochondrial complex IV activity. Control = untreated RPE cells; NtBHA = RPE cells treated with 250 µM NtBHA; FAC, 4 days = RPE cells treated with 250 µM FAC for 4 days; FAC + 0 µM NtBHA = RPE cells treated with 250 µM FAC for 4 days, then treated with NtBHA-free cell medium; FAC + 250 µM NtBHA = RPE cells treated with 250 µM FAC for 4 days, then treated with 250 µM NtBHA. Changes in the enzyme activity were measured using kinetic colorimetric assay. FAC treatment for 4 days caused a significant decrease in complex IV activity. Treatment with 250 µM NtBHA of iron overloaded cells resulted in a significant increase of complex IV activity compared with RPE cells treated with medium alone (0 µM NtBHA). Iron-loaded RPE cells treated with 250 µM NtBHA demonstrated significantly higher levels of complex IV activity compared with RPE cells treated with medium alone (0 µM NtBHA). The data represent mean ± sd of 3 independent experiments (*P<0.05 vs. control, **P<0.01).