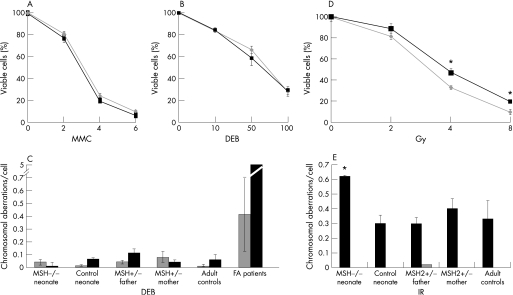
Figure 2 Sensitivity and DNA damage after exposure to interstrand cross‐linking agents and ionising radiation. Survival, expressed relative to untreated cells, of homozygous MSH2 226C→T fibroblasts (grey lines and diamonds) and control neonate fibroblasts (black squares and lines) after exposure to micromolar concentrations shown of (A) mitomycin C (MMC), (B) 1,2,3,4‐diepoxybutane (DEB) or (D) ionising radiation. Each experiment was performed in triplicate and the standard deviation about the mean for three experiments is shown. *Significant difference for cell viability between groups (p<0.001, t test). The average number of chromosome aberrations per cell in peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) from family members and controls is shown in the absence of treatment (grey) or after exposure to DNA‐damaging agents (black). (C) 0.1 μg/ml DEB, (E) 3 Gy ionising radiation: 25 metaphase spreads were examined for each case and standard error about the mean for two experiments is shown for family member samples. The average and standard error is shown for aberrations/cell from PBLs of (C) 38 normal adult and 28 Fanconi anaemia patients, and (E) 10 normal adult controls. *Significant difference in chromosome aberrations after treatment (p<0.05, unpaired Mann‐Whitney test).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.