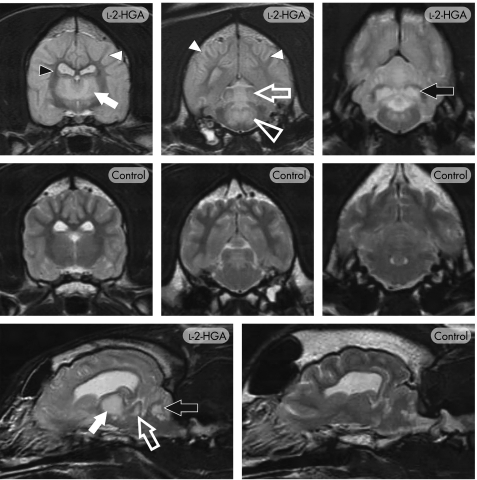
Figure 2 T2‐weighted MRI of canine l‐2‐hydroxyglutaric aciduria (l‐2‐HGA). Transverse images through the level of the thalamus, midbrain and cerebellum (top and middle panels) and para‐sagittal images (bottom panel) in an affected (l‐2‐HGA) and normal (control) Staffordshire bull terrier. Extensive, bilaterally symmetrical increased signal is present, particularly affecting the cerebral cortex, cerebral white matter (white arrowheads), thalamus (closed white arrow), caudal colliculi (open white arrow), dorsomedian tegmentum (open white arrowhead) and the cerebellar nuclei (black arrow), including the dentate nucleus. The central region of the internal capsule (small black arrowhead) and the corpus callosum retained the normal white‐matter signal.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.