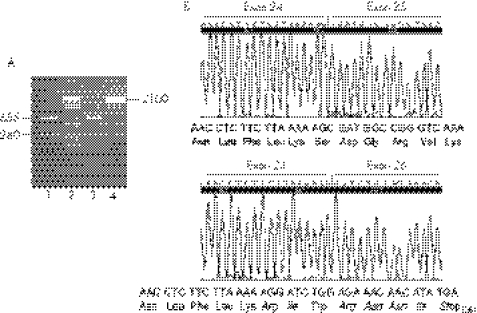
Figure 1 Apolipoprotein (apo)B mRNA in the liver of proband familial hypobetalipoproteinaemia (FHBL)‐20, heterozygotic for the c.3843−2A→G mutation in intron 24. (A) Agarose gel electrophoresis of the reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction (RT‐PCR) amplification of apoB cDNA region spanning from the 3′‐end of exon 24 to the 5′‐end of exon 26. Lane 1: proband; lane 2: DNA size marker; lane 3: control; lane 4: PCR product of the same APOB gene region amplified from genomic DNA. (B) Electropherograms of a partial sequence of the two apoB cDNAs present in the proband's liver. The upper panel shows the sequence of the normal 655 bp RT‐PCR fragment, encompassing the junction between exons 24 and 25; the lower panel shows the sequence of the abnormal 280 bp RT‐PCR fragment, encompassing the junction between exons 24 and 26. This junction produces a frameshift, leading to the insertion of seven novel amino acids (in italics) and a premature stop codon.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.