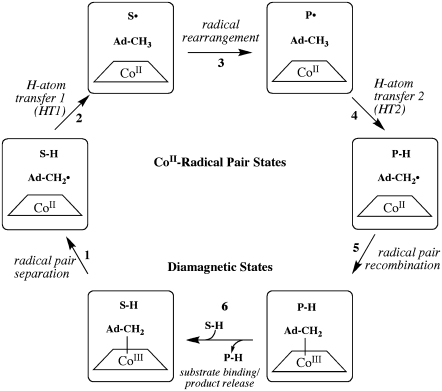
FIGURE 1.
Minimal mechanism of catalysis for coenzyme B12-dependent EAL (29,30). The forward direction of reaction is indicated by arrows. The steps are: (1) radical pair separation, (2) first hydrogen atom transfer (HT1), (3) radical rearrangement, (4) second hydrogen atom transfer (HT2), (5) radical pair recombination, and (6) product release/substrate binding. Substrate-derived species are designated S-H (bound substrate), S· (substrate radical), P· (product radical), and PH (diamagnetic products). The 5′-deoxyadenosyl β-axial ligand is represented as Ad-CH2 in the intact coenzyme, and as 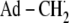 (5′-deoxyadenosyl radical) or Ad-CH3 (5′-deoxyadenosine) after cobalt-carbon bond cleavage. The cobalt ion and its formal oxidation states are depicted, but the corrin ring and the dimethylbenzimidazole α-axial ligand of the coenzyme (68,69) are not shown for clarity.
(5′-deoxyadenosyl radical) or Ad-CH3 (5′-deoxyadenosine) after cobalt-carbon bond cleavage. The cobalt ion and its formal oxidation states are depicted, but the corrin ring and the dimethylbenzimidazole α-axial ligand of the coenzyme (68,69) are not shown for clarity.