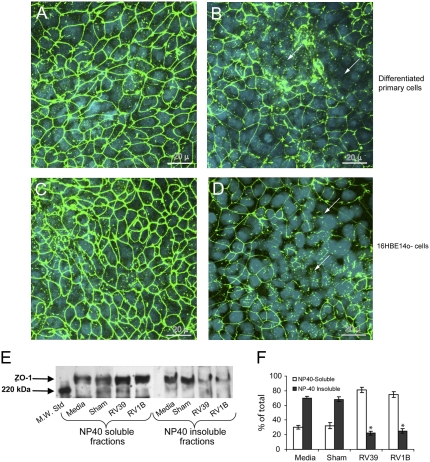
Figure 7.
Rhinovirus (RV) infection reduces transepithelial resistance by dissociating zona occludins (ZO)-1 from tight junction complex. Well-differentiated (A and B) primary or (C and D) polarized 16HBE14o- human bronchial epithelial cells were infected with either (A and C) sham or (B and D) RV39 and incubated for 24 hours as described above. Cells were fixed in cold methanol and immunostained with antibody to ZO-1 (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). Arrows represent dissociation of ZO-1 from the tight junction complex. NP40 soluble and insoluble fractions from medium-treated, sham, RV39, or RV1B-infected polarized 16HBE14o- cells were subjected to Western blot analysis with (E) antibody to ZO-1. (F) A representative blot from three independent experiments is presented. Group mean data from three independent experiments (bars represent mean ± SEM; P < 0.05, analysis of variance).