Abstract
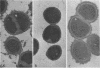
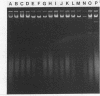
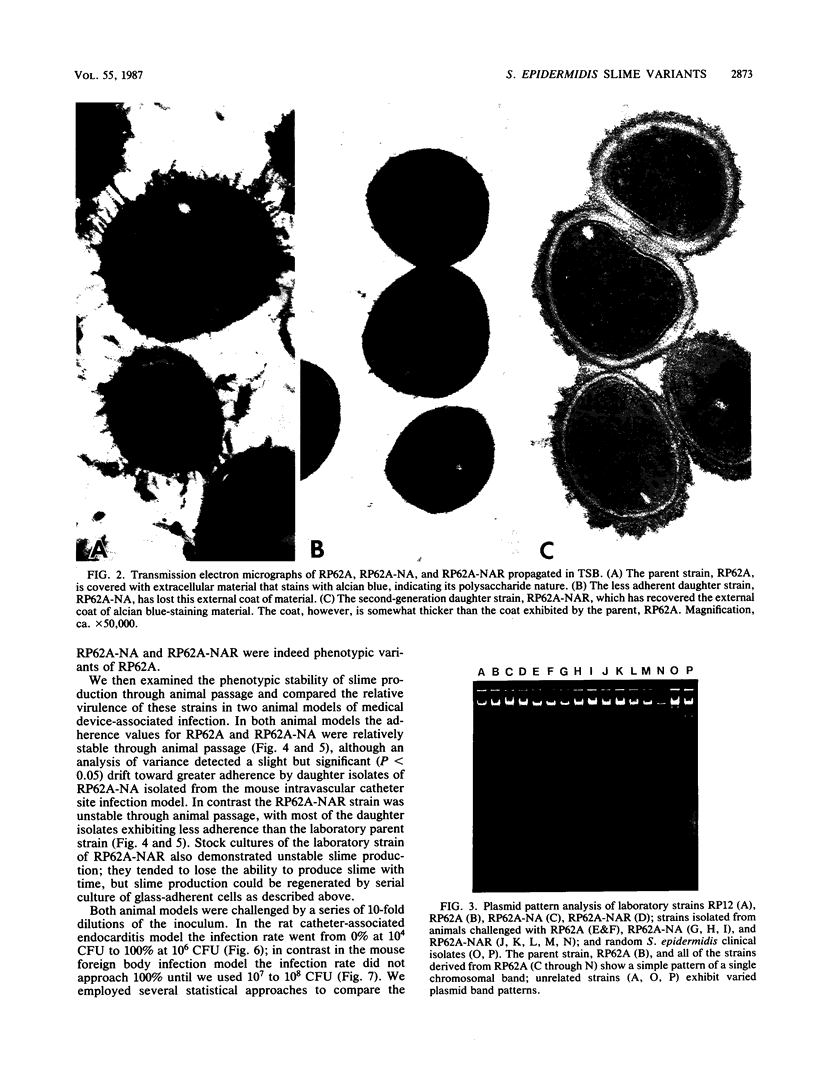
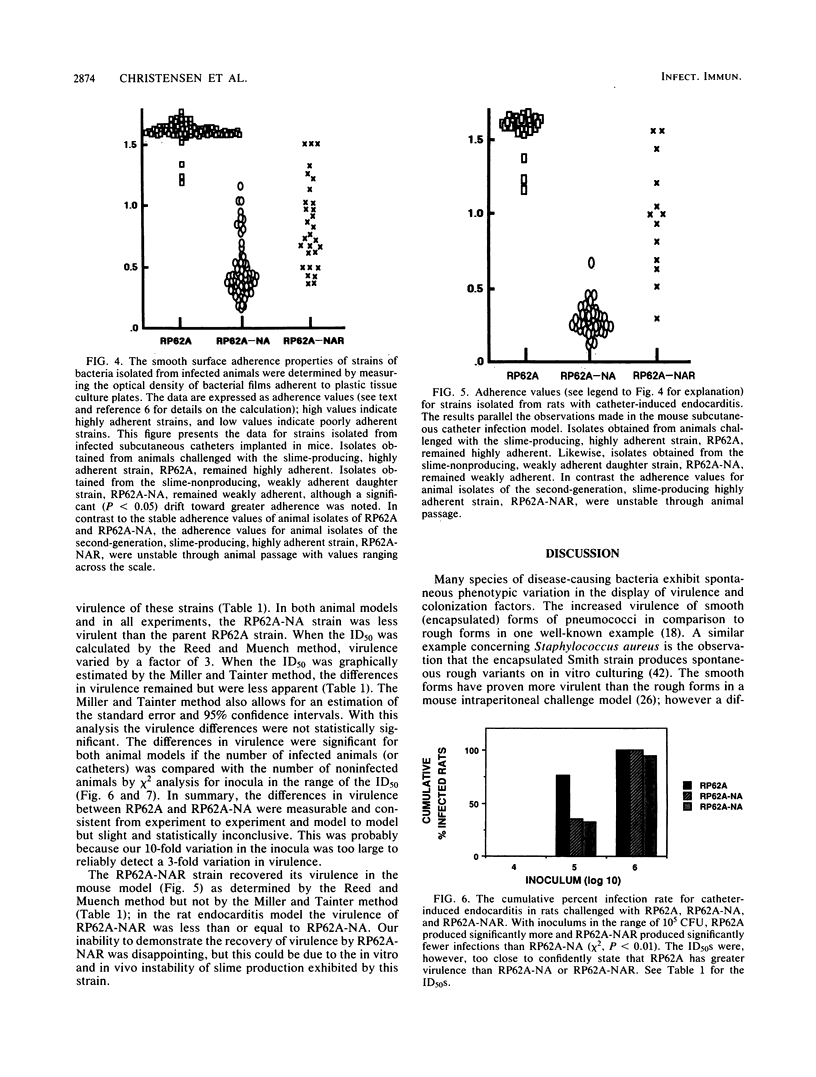
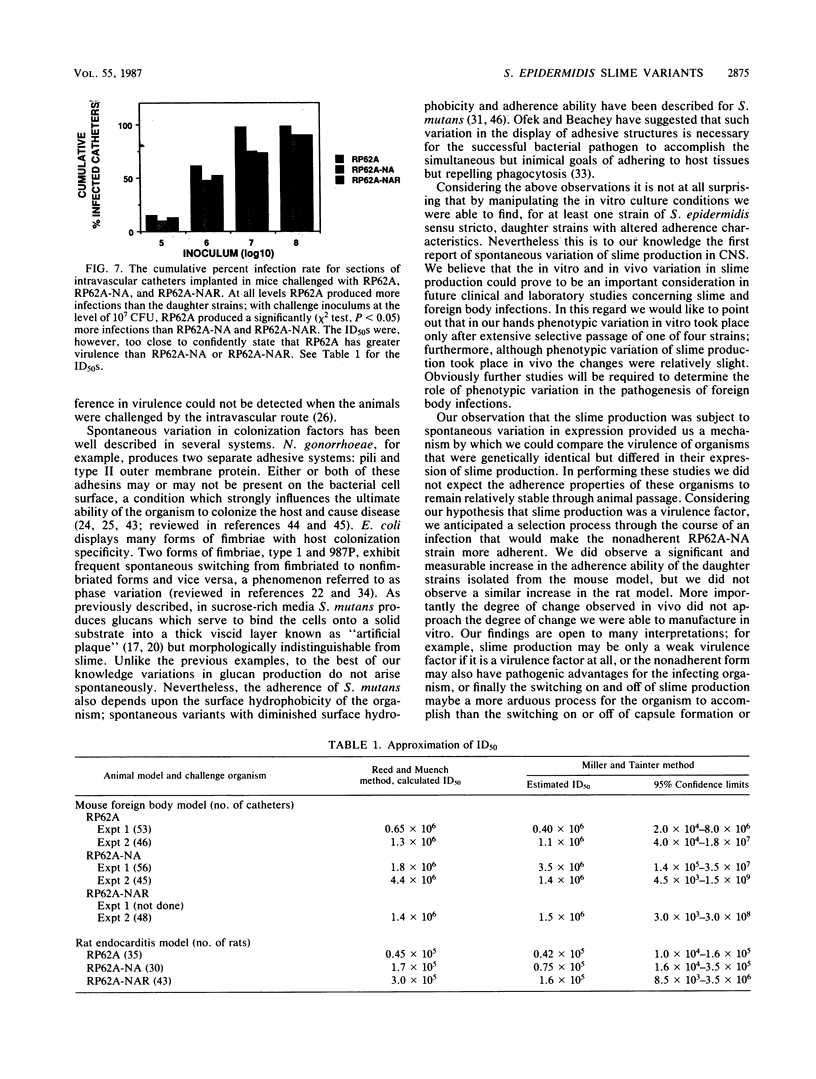
Clinical studies performed by us and others have found an association between slime production and strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci that infect indwelling medical devices. By serial low-speed centrifugation of broth cultures we have isolated a stable, weakly adherent strain (RP62A-NA) from a strongly adherent, slime-producing, pathogenic strain of Staphylococcus epidermidis sensu stricto (RP62A, ATCC 35984). We obtained a second strain from RP62A-NA (RP62A-NAR) by serial subculture of glass-adherent cells of RP62A-NA. All three strains had the same pattern of biochemical reactions, antimicrobial susceptibilities, and plasmid analysis. Transmission electron micrograph sections stained with the mucopolysaccharide-specific stain alcian blue demonstrated that the adherent strains RP62A and RP62A-NAR were covered with an extracellular coat of polysaccharide-rich material. In contrast, the nonadherent RP62A-NA strain lacked this external coat. All three strains were used in a mouse model of foreign body infection and a rat model of catheter-induced infective endocarditis. The adherence characteristics of isolates of RP62A and RP62A-NA recovered from experimental animals were relatively stable, although we noted a slight but a significant increase in the adherence of RP62A-NA isolates recovered from the foreign body model. The adherence characteristics of RP62A-NAR isolates recovered from infected animals were variable; in general these isolates were less adherent than the laboratory strain of RP62A-NAR. In both models the 50% infective dose (calculated by the Reed and Muench method) was three times greater for the RP62A-NA strain than for the RP62A strain. The phenotypic expression of slime production is subject to both in vitro and in vivo variation and could play a role in the pathogenesis of foreign body infection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L., Karchmer A. W., Vishniavsky N., Johnston J. L. Plasmid-pattern analysis for the differentiation of infecting from noninfecting Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):913–920. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Christensen G. D., Bisno A. L. Bacterial concentration correlations in experimental endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):207–210. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.207-210.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Christensen G. D., Hester M. G., Bisno A. L. Production of experimental endocarditis by coagulase-negative staphylococci: variability in species virulence. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):721–727. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Smalley D. L., Kraus A. P., Jr, Lamoreaux W. J., Christensen G. D. Comparison of microbiologic characteristics of pathogenic and saprophytic coagulase-negative staphylococci from patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;5(3):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayston R., Penny S. R. Excessive production of mucoid substance in staphylococcus SIIA: a possible factor in colonisation of Holter shunts. Dev Med Child Neurol Suppl. 1972;27:25–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1972.tb09769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Bisno A. L., Parisi J. T., McLaughlin B., Hester M. G., Luther R. W. Nosocomial septicemia due to multiply antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jan;96(1):1–10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Parisi J. T., Bisno A. L., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Characterization of clinically significant strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):258–269. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.258-269.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Experimental foreign body infections in mice challenged with slime-producing Staphylococcus epidermidis. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):407–410. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.407-410.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Younger J. J., Baddour L. M., Barrett F. F., Melton D. M., Beachey E. H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):996–1006. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.996-1006.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D. The confusing and tenacious coagulase-negative staphylococci. Adv Intern Med. 1987;32:177–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport D. S., Massanari R. M., Pfaller M. A., Bale M. J., Streed S. A., Hierholzer W. J., Jr Usefulness of a test for slime production as a marker for clinically significant infections with coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):332–339. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson T. R., Sheth N. K., Rose H. D., Sohnle P. G. Scanning electron microscopy of bacteria adherent to intravascular catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.500-505.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerina N. G., Kessler T. W., Guerina V. J., Neutra M. R., Clegg H. W., Langermann S., Scannapieco F. A., Goldmann D. A. The role of pili and capsule in the pathogenesis of neonatal infection with Escherichia coli K1. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):395–405. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. P., Hamory B. H., Parisi J. T., Strausbaugh L. J. Staphylococcus epidermidis arthritis following catheter-induced bacteremia in a neutropenic patient. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;3(2):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(85)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak M. A., Gröschel D. H., Mandell G. L., Wenzel R. P. Association of slime with pathogenicity of coagulase-negative staphylococci causing nosocomial septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1025–1029. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1025-1029.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G. Factors relating to the virulence of staphylococci. I. Comparative studies on two colonial variants. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Jun;34:537–559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E., James L. T., Watt P. J. Variations in surface protein composition associated with virulence properties in opacity types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):305–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Costerton J. W. Morphology of bacterial attachment to cardiac pacemaker leads and power packs. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):911–914. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.911-914.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Costerton J. W. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy of in situ bacterial colonization of intravenous and intraarterial catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):687–693. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.687-693.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Noble M. A., Costerton J. W. Examination of the morphology of bacteria adhering to peritoneal dialysis catheters by scanning and transmission electron microscopy. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1388-1398.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Song M., Krasse B., Olsson J. Biochemical and immunological differences between hydrophobic and hydrophilic strains of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):68–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.68-75.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchison H., Larrimore S., Curtiss R., 3rd Isolation and characterization of Streptococcus mutans mutants defective in adherence and aggregation. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):1044–1055. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.1044-1055.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Adherence and growth of coagulase-negative staphylococci on surfaces of intravenous catheters. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):479–482. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Microbial colonization of prosthetic devices. II. Scanning electron microscopy of naturally infected intravenous catheters. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1981;173(5):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Saborowski F., Locci R., Pulverer G. Investigations on staphylococcal infection of transvenous endocardial pacemaker electrodes. Am Heart J. 1984 Aug;108(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90625-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro J., Levison M. E. Rat model of experimental endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):915–918. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.915-918.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Parisi J. T., Vidal L., Baldwin J. N. Nature of the genetic determinant controlling encapsulation in Staphylococcus aureus Smith. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):231–234. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.231-234.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergren G., Olsson J. Hydrophobicity and adherence of oral streptococci after repeated subculture in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):432–435. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.432-435.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younger J. J., Christensen G. D., Bartley D. L., Simmons J. C., Barrett F. F. Coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from cerebrospinal fluid shunts: importance of slime production, species identification, and shunt removal to clinical outcome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):548–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]