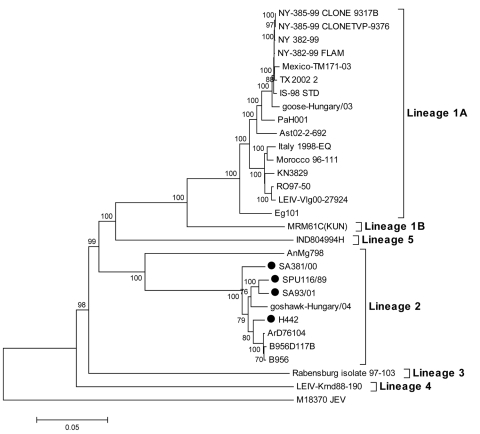
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of full genome nucleotide sequences of lineage 1 and 2 strains of West Nile virus. The tree was constructed by using MEGA version 3.1 (13) with the neighbor-joining method and Kimura 2-parameter distance matrix. A bootstrap confidence level of 1,000 replicates was used. South African strains sequenced in this study are indicated by a black circle. GenBank accession nos. are as follows: NY-385–99 clone 9317B (DO66423), NY-385–99 clone TVP-9376 (AY848697), NY 385–99 (DQ211652), NY-382–99 FLAM (AF196835), IS-98 STD (AF481864), Mexico-TM171–03 (AY660002), TX 2002 2, (DQ 164205), goose-Hungary/03 (DQ 118127), Eg 101 (AF 260968), RO97–50 (AF260969), Morocco 96–111 (AY701412), Italy 1998-Eq (AF 404757), KN3829 (AY262283), LEIV-Vlg00–27924 (AY278442), PaH001 (AY268133), Ast02–2-696 (DQ411035), MRM61C (KUN) (D00246), IND804994H (DQ 256376), AnMg798 (DQ 176636), SA381/00 (EF429199), H442 (EF429200), goshawk-Hungary/04 (DQ 116961), SPU116/89 (EF429197), SA93/01 (EF429198), B956D117B3 (M12294), B956 (AY532665), ArD76104 (DQ 318019), Rabensburg isolate 97–103 (AY765264), LEIV-Krnd88–190 (AY277251), and M18370 JEV (M18370).