Figure 1.
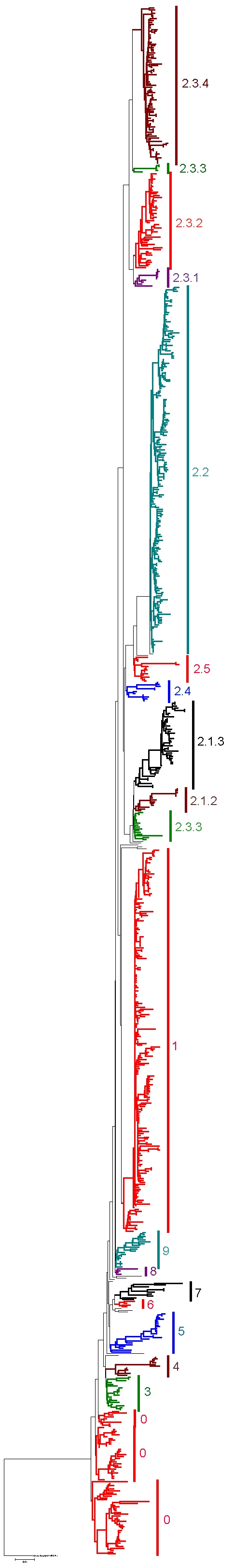
Neighbor-joining tree of 859 H5N1 isolates constructed by using PAUP* version 4.0b10 (9) with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. The tree was rooted by using the highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (H5N1) strain A/turkey/England/50–92/91, a historical European H5N1 virus closely related to the Gs/GD lineage (10). Clades are color coded with isolates not given a clade designation in light green. Maximum-likelihood trees used for comparison were constructed by using GARLI version 0.951 (11). Bayesian analysis for comparison was conducted with MrBayes version 3.1 (12) by using 4 replicates of 2 million generations, sampled every 100 generations, with 6 chains. The convergence of Markov Chain Monte Carlo chains was confirmed for each dataset by using Tracer version 1.3 (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/tracer). Estimates of the statistical significance of phylogenies were calculated by performing 1,000 NJ bootstrap replicates, and Bayesian posterior probabilities were calculated from the consensus of 60,000 trees after excluding the first 20,000 trees (25%) as burn-in. Scale bar represents 0.01-nt changes.
