Fig. 1.
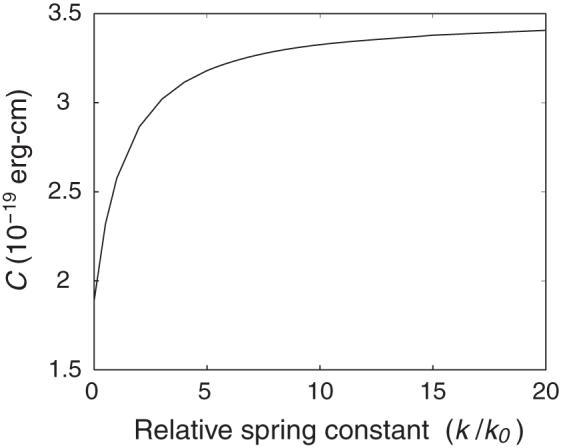
Dependence of the torsional modulus of a generic, naturally straight DNA homopolymer on the relative spring constant k/k0 used to restrain the chain ends at the equilibrium end-to-end distance. Here k0 is the force constant, defined by (6), which keeps neighboring base pairs at their van der Waals’ separation distance . Three coupling interactions (f23, f25, f36)—Roll-Twist, Twist-Slide, and Twist-Rise—are incorporated into the internal energy function.
